Cost Per Order: Definition, Calculation & 8 Best Tips 2026

Cost per order (CPO) measures the cost of fulfilling a single customer order, including product, shipping, and marketing expenses. It directly impacts your profitability—if CPO is too high, you could lose money on each sale. By tracking and optimizing CPO, you can make better pricing decisions, improve efficiency, and increase profits.
In this article, we will discuss how to determine the real average amount of money you have to pay per order and tips on how to minimize it to maximize profits. Scroll on!
In this blog:
What Is Cost Per Order?
Cost Per Order (CPO) is the total cost incurred every time a customer places an order in your online store. It includes all the expenses involved in selling a product, such as product cost, shipping, marketing, and transaction fees.
Understanding your CPO is crucial for measuring profitability. If your CPO is too high, your profit margins shrink even if sales are booming. By optimizing CPO, you can maximize profits without necessarily increasing sales volume.
Why Is The Cost Per Order Important?
1. Optimize customer acquisition budget
Knowing your CPO helps you avoid spending more on acquiring customers than they’re worth. It shows your profit per order after all costs, ensuring your marketing spend is effective.
2. Evaluate Marketing Campaigns
CPO lets you easily compare the cost-effectiveness of different marketing channels, such as Facebook ads, Google ads, or banner ads.
3. Data-driven Growth
Accurate CPO tracking prevents guesswork and helps you scale sustainably. By understanding your CPO, you can pinpoint cost-saving opportunities and reinvest in growth strategies like product development or enhanced branding.
How to Calculate Cost Per Order?
Calculating CPO is straightforward with this formula:
Here's a breakdown of the costs typically included:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The direct cost of the product, including manufacturing and shipping from the supplier.
- Marketing Costs: Expenses from advertising campaigns, social media promotions, or influencer collaborations.
- Shipping and Fulfillment: Costs for packaging, shipping, and third-party logistics services.
- Transaction Fees: Payment processing fees, like those from Shopify Payments or PayPal.
Why CPO Alone Isn’t Enough?
While CPO tells you how much each order costs, it doesn’t show you whether you’re actually making a profit. To understand this, you need to look at how much revenue you’re earning per order by calculating your Average Order Value (AOV):
Once you have your AOV, you can calculate your average profit per order:
This helps you evaluate your profitability. If your CPO is higher than your AOV, or if your profit per order is lower than your expected profit margin, you may need to adjust your pricing strategy or cut costs.
Now that you know how to calculate your Cost Per Order, it's essential to understand how it affects your profit margin. Use our free Profit Margin Calculator to see your earnings and optimize your pricing strategy.
8 Practical Tips to Minimize Your CPO
Reducing your Cost Per Order (CPO) isn’t just about cutting expenses—it’s about streamlining operations and maximizing profitability. Here are 8 actionable tips to help you minimize your CPO and boost your bottom line.
1. Speed Up Order Processing
Faster order processing reduces labor costs and improves customer satisfaction. Here’s how to do it:
- Streamline Workflows: Use barcode scanner to identify products and reduce manual work. By scanning items during picking, packing, and shipping, you can instantly get encoded product details accurately.
- Standardize Operating Procedures: Define clear responsibilities, set priorities, and monitor performance.
- Optimize Picking and Packing: Utilize the right equipment and organize your packing area efficiently.
- Conduct Quality Checks: Verify order accuracy, quantity, and quality before shipping.
- Strategic Warehouse Layout: Place fast-moving items near packing stations and maximize space with vertical racks.
- Efficient Packaging: Use appropriately sized packaging and consider branded elements for a better unboxing experience.
- Accurate Shipping Labels: Choose clear fonts and barcodes, and select the most cost-effective shipping method.
2. Offer free shipping at certain minimum orders
Free shipping is a powerful incentive, but it can increase your CPO if not managed carefully.
Set a minimum order threshold for free shipping. This encourages customers to spend more, helping you offset shipping costs while boosting your average order value (AOV).
3. Implement the multi-node fulfillment strategy
What is Multi-Node Fulfillment?
This strategy involves fulfilling and shipping orders from multiple locations closer to your customers.
Benefits:
- Reduced Shipping Costs: By minimizing delivery zones, you cut down on shipping expenses.
- Faster Delivery Times: Shorter distances mean quicker deliveries, enhancing customer satisfaction.
4. Leverage your customer insights
Why It Matters:
Understanding your customers’ buying behaviors helps you stock inventory more efficiently, reducing storage and overstock costs.
How to Do It:
- Analyze Purchase Patterns: Identify popular products and stock them accordingly.
Targeted Marketing: Use customer data to create personalized marketing campaigns, increasing conversion rates and AOV.
5. Outsource non-core tasks
Focus on Growth:
Outsourcing tasks like customer support, payment processing, and account management helps you lower operational costs while maintaining quality.
Benefits:
- Cost Savings: Pay only for the services you need, reducing overhead costs.
- Scalability: Easily scale operations during peak seasons without hiring additional staff.
6. Build upselling and cross-selling campaigns
Your cost per order in eCommerce can be considerably influenced by the average order value.
Therefore, you need to develop cross-sells and upsells that are specifically catered to your customers to improve your Shopify average order value.
How to Increase AOV to Lower CPO:
- Bundle Products: Offer complementary products at a discounted rate.
- Personalized Recommendations: Use purchase history to suggest relevant items.
7. Optimize your marketing plan
E-commerce ads drive sales but can be costly if not optimized. With an average CAC of $58.64 per new customer, it's a major factor in your cost per order. To reduce CPO, start by refining your marketing strategy.
Actionable Tips:
- Leverage Retargeting: Re-engage potential customers who abandoned carts.
- Focus on Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): Develop campaigns that encourage repeat purchases. Instead of relying on an ad to bring people just once, you need to create campaigns that encourage them to make more purchases or repeat purchases over time. Check out our article on how to increase customer lifetime value.
8. Lower product returns
Returns not only affect profitability but also impact customer satisfaction. Here are 4 tips to reduce returns:
- Accurate Product Descriptions: Provide detailed product information to set customer expectations.
- Quality Control Checks: Ensure items are accurate and undamaged before shipping.
- Effective Return Policies: Make return policies clear and easy to understand, reducing confusion and potential disputes.
- Secure Packaging: Use durable packaging to protect products during transit.
Final Thoughts
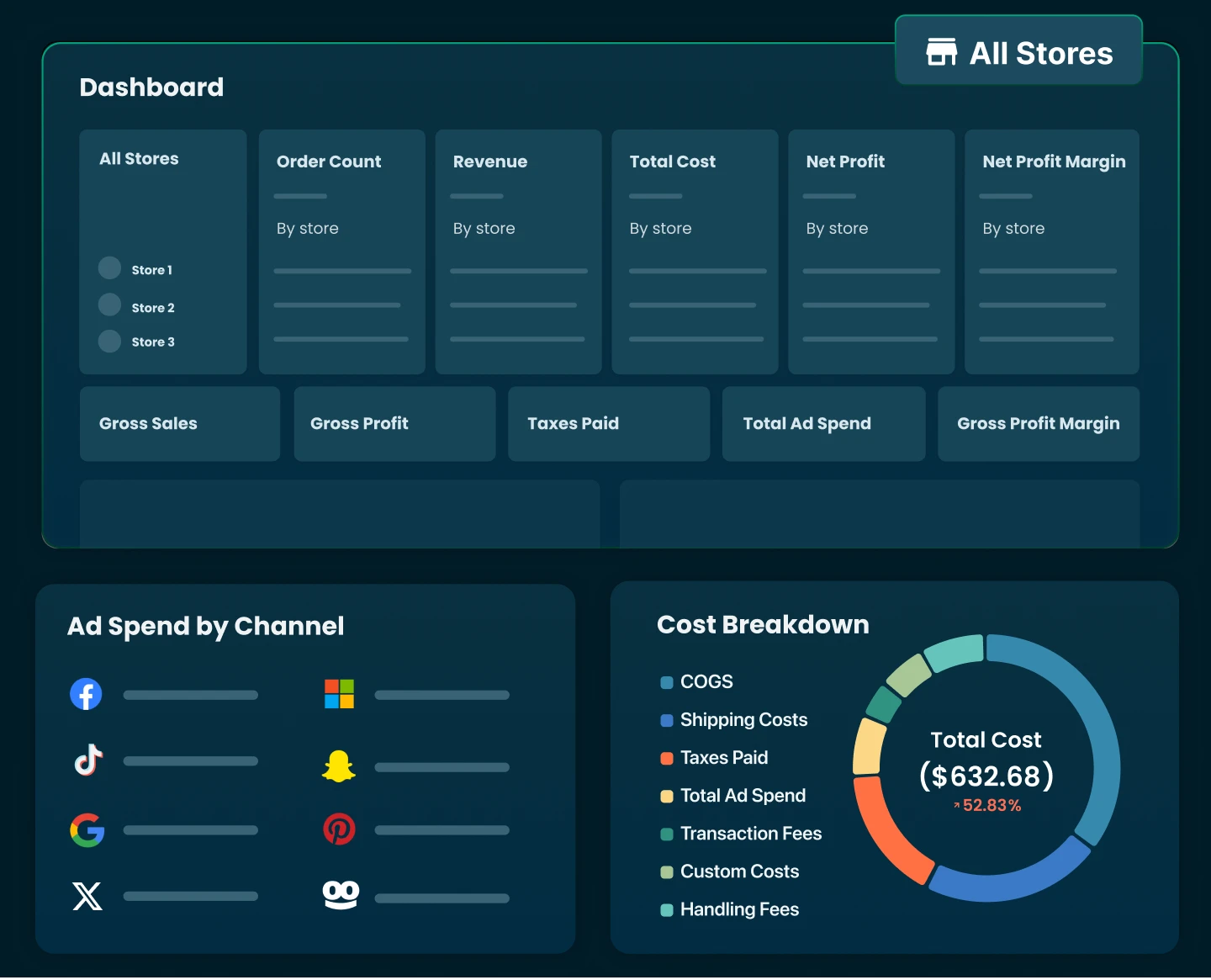
Understanding cost per order is critical to your store’s success. But calculating and tracking them manually? That’s time-consuming and prone to errors.
With TrueProfit, you can instantly access all your essential metrics in one place - no spreadsheets, no stress. Join thousands of Shopify merchants who have unlocked a clearer view of their net profit with our real-time profit tracking solution.
Harry Chu is the Founder of TrueProfit, a net profit tracking solution designed to help Shopify merchants gain real-time insights into their actual profits. With 11+ years of experience in eCommerce and technology, his expertise in profit analytics, cost tracking, and data-driven decision-making has made him a trusted voice for thousands of Shopify merchants.








 Shopify profits
Shopify profits