Net Profit Margin 101: Definition, Formula & Insights (2026)

Net profit margin shows how efficiently your business turns revenue into profit after covering all expenses. It directly impacts your bottom line and reveals how well you’re managing costs and pricing strategies.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about this essential profitability metric and how it impacts your business's success.
In this blog:
What Is Net Profit Margin?
Net profit margin measures how much profit your business makes as a percentage of total revenue. It’s calculated by dividing Net Profit by Net Revenue.
Typically shown as a percentage (%), it reveals how effectively your business turns revenue into profit after all expenses, including operational costs, interest, and taxes.
- High Net Profit Margin: Shows efficient cost control, smart resource allocation, and an effective pricing strategy.
- Low Net Profit Margin: Indicates challenges in growing sales or managing expenses.
This metric helps you understand your business's profitability and cost efficiency. To get a clear picture of your net profit margin, it's essential to calculate your cost of order accurately, as it directly impacts your profitability.
How to Calculate Net Profit Margin?
The formula for calculating net profit margin is straightforward:
To break this down, net sales is your total revenue minus any returns, allowances, and discounts. Hence, net profit margin can also be calculated like below:
Want a quick check up? Check out our free profit margin calculator.
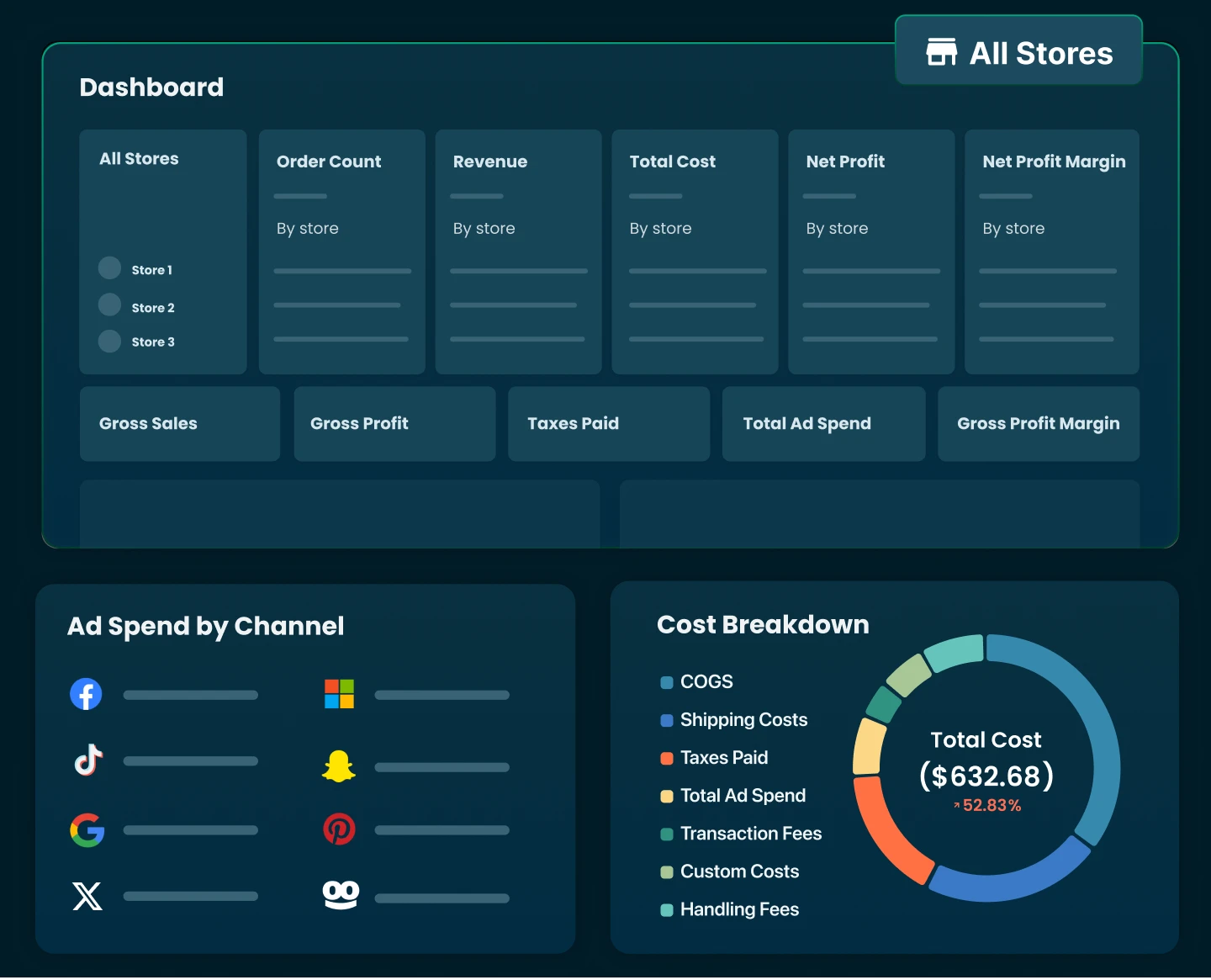
If you’re a Shopify store owner, install TrueProfit > Go to ‘P&L Report’ to instantly see your latest net profit margins and all your store’s crucial metrics in real time now!
A Real-life Example Of Net Profit Margin
To have a better grasp of the metric, let's calculate the net profit margin of a real business entity. Here is the consolidated income statement from IKEA - a giant furniture company based in the Netherlands.
- Net Income: €1,443 million
- Total Revenue: €25,615 million
Using the formula:
- Net Profit Margin = (€1,443m / €25,615m) x 100% = 5.63%
This means that for every euro IKEA earns in revenue, approximately €0.0563 is profit. In other words, IKEA keeps 5.63 cents for every €1 in sales after covering all expenses. This shows how efficiently they manage costs, helping you understand how to maximize profit by controlling expenses.
What Is a Good Net Profit Margin?
There is no universal standard for a "good" net profit margin, as it varies significantly by industry. To evaluate your margin’s effectiveness, compare it with competitors within the same niche:
- Household Products: An average net profit margin is around 11.25%, so IKEA’s 5.63% is slightly below the industry average.
- Apparel Brands: Average around 5.07%, so a 10% margin in this sector would be considered high.
Benchmarks like these help you assess your performance accurately.
The data in the example above is from the net profit margin benchmark report by industry by New York University on 5,500+ US-based businesses as of January 2026.
How to Boost Your Net Profit Margin?
To improve your net profit margin, you can either:
- Increase Sales – But this typically requires more investment in marketing and expansion, leading to higher costs.
- Decrease Costs – Be cautious not to compromise product quality, as it may negatively impact customer retention.
Tip: Invest in long-term branding strategies. Businesses with strong brand value can justify premium pricing, thereby enhancing profit margins without drastically cutting costs.
Three Limitations Of Net Profit Margin
No metric can give you a complete and clear picture of your business’s financial health. Net profit margin is no exception. While net profit margin is a crucial profitability metric, it has three limitations:
Lacks Cash Flow Insight: It shows profitability as a percentage but doesn't reveal the actual profit amount or cash flow. For example:
Company A: Net Profit Margin = 10% ($1,000 / $10,000)
Company B: Net Profit Margin = 5% ($5,000,000 / $100,000,000)
-> Despite a lower margin, Company B earns substantially more profit.
Sensitive to Income Statement Changes: One-time expenses or investments can significantly impact net profit margin, giving a skewed perspective on profitability.
Not Always Relevant for New Businesses: For startups in the growth or expansion stage, net profit margin might be low due to heavy marketing and infrastructure investments.
Net Profit Margin Impact for New Businesses
Many new businesses overlook certain expenses, leading to inaccurate net profit margin calculations. Avoid common pitfalls by understanding the mistakes to avoid when calculating profit for your Shopify store.
On top of that, aiming for a high net profit margin shouldn’t be top priority for new businesses. Instead, your focus should be on growth and market share. Let’s take a look at the business cycle model below:


When you’re just starting out, you’ll likely invest heavily in paid advertising, SEO, and other marketing efforts to build brand awareness and capture market share. At this expansion stage, prioritizing growth over profitability is essential to establish your presence in the market.
Similarly, during a recession phase, it’s more strategic to invest in infrastructure and diversify your product offerings to prepare for future growth. In both scenarios, chasing a high net profit margin can limit your ability to scale effectively.
For dropshipping businesses, maintaining a healthy net profit margin can be challenging due to high competition and advertising costs. Learn more about optimizing your dropshipping profit margin to maximize your profitability.
Net Profit Margin vs. Gross Profit Margin & Other Margins
Net profit margin is the most comprehensive metric because it considers all costs involved in generating sales, including COGS, operating expenses, interest, and taxes.
In contrast:
- Gross Profit Margin: Only accounts for COGS, excluding operating and non-operating expenses.
- Operating Margin: Includes operating costs but omits non-operating costs.
Net profit margin is a vital metric for assessing your profitability. However, it should not be viewed in isolation. For a full picture of your business's financial performance, consider other key metrics like cash flow, gross profit margin, and operating margin.
But calculating and tracking them manually? That’s time-consuming and prone to errors.
With TrueProfit, you can instantly access all your essential metrics in one place - no spreadsheets, no stress. Join thousands of Shopify merchants who have unlocked a clearer view of their net profit with our real-time profit tracking solution.
Harry Chu is the Founder of TrueProfit, a net profit tracking solution designed to help Shopify merchants gain real-time insights into their actual profits. With 11+ years of experience in eCommerce and technology, his expertise in profit analytics, cost tracking, and data-driven decision-making has made him a trusted voice for thousands of Shopify merchants.








 Shopify profits
Shopify profits