Gross Profit Margin: Definition, Formula, Example & More!
Gross profit margin shows how much profit you make from each dollar of revenue after taking out the cost of goods sold. It helps you evaluate your pricing strategy and control your goods costs.
But you might be wondering:
- What exactly is the gross profit margin?
- How do you calculate it?
- Why should you track it?
- How does it differ from net profit margin or operating margin?
Don’t worry - this article covers all of that and more. Let’s dive in!
In this blog:
What Is Gross Profit Margin?
Gross profit margin is a vital profitability metric that shows you how much percent of your revenue is left after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). The metric is presented under percentage value (%).
A high gross profit margin indicates that your business can significantly profit from its sales. In contrast, a low gross margin suggests that you might struggle to keep your direct costs at bay or face pricing pressure from competitors.
Why Is Gross Profit Margin Important?
Tracking your gross profit margin regularly helps you:
- Assess Pricing Strategy: Ensure that your product prices are high enough to cover costs while remaining competitive.
- Control Costs: Identify rising COGS and take action, such as negotiating with suppliers or optimizing production.
- Measure Efficiency: Understand how efficiently your business produces goods compared to revenue generation.
Improve Profitability: Make data-driven decisions to enhance your overall profitability.
How to Calculate Gross Profit Margin?
Calculating gross profit margin is straightforward. Use the following formula:
Since gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue, the formula can also be written as:
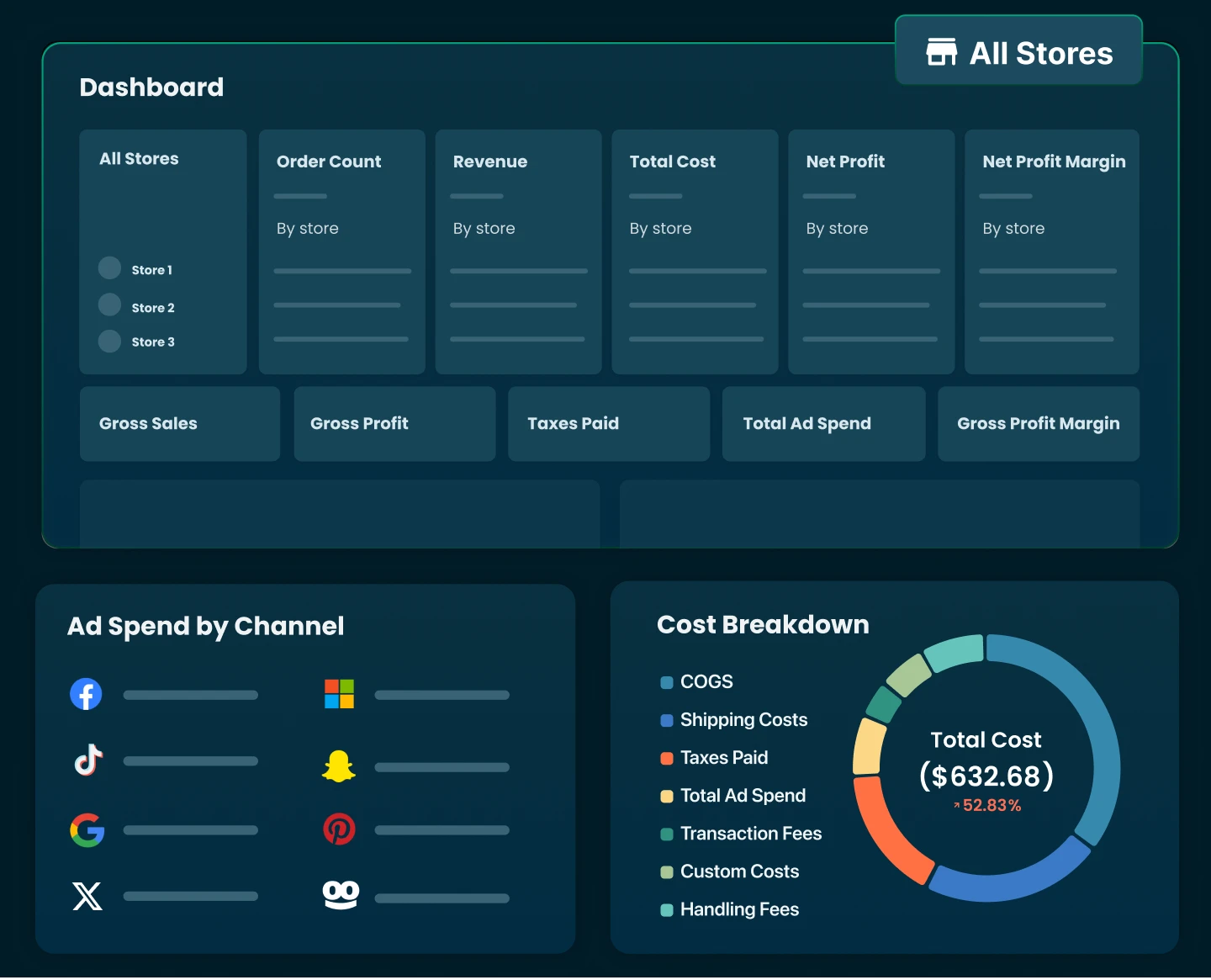
If you’re a Shopify store owner, install TrueProfit > Go to ‘Profit & Loss Report’ so you can instantly see your gross margins and all your store’s crucial metrics in real time.
A Real-life Example Of Gross Profit Margin
To better understand gross profit margin, let’s look at IKEA, the global furniture giant. Below is the company's consolidated income statement for the fiscal year 2021:
To calculate the gross profit margin for IKEA, we would simply divide the gross profit by the total revenue and multiply it by 100%.
So the gross profit margin for this company is 17.48%. This means that for every euro of revenue, the company keeps 17.48 cents in gross profit before taking into account other business expenses.
What Is a Healthy Gross Profit Margin?
A gross profit margin between 30-40% is generally considered healthy for e-commerce. This range allows enough room to cover other expenses like marketing, shipping, and platform fees while maintaining profitability.
However, gross profit margins can vary widely depending on the type of products you sell. Digital products and branded merchandise often have higher margins since they have lower costs of goods sold (COGS). In contrast, electronics and consumer goods usually have thinner margins due to intense competition and fluctuating supplier costs.
To know if your gross profit margin is competitive, compare it with industry benchmarks within your specific product category. This will help you understand where you stand and if there’s room for improvement.
How to Improve Your Gross Profit Margin?
Improving your gross profit margin is essential for maintaining a sustainable business, funding growth opportunities, and boosting overall profitability. Here are 5 effective strategies:
- Increase Prices: Carefully raise prices to boost margins without losing customers.
- Reduce Costs: Cut expenses by negotiating with suppliers, minimizing waste, and optimizing inventory.
- Enhance Efficiency: Streamline operations and automate tasks to reduce labor costs and increase productivity.
- Focus on High-Margin Products: Promote high-margin items and reconsider low-margin offerings.
Upsell and Cross-Sell: Boost revenue by encouraging customers to buy complementary or premium products.


Three Limitations Of Gross Profit Margin
Although the gross margin is a useful financial metric, you should note that the stand-alone gross profit margin won't give you a clear and complete picture of your business's financial health performance.
Particularly, here are three limitations of gross profit margin:
- Ignore Other Expenses: It only considers revenue and COGS, overlooking other costs like marketing, R&D, and overheads. A high gross margin doesn’t always mean high net profit.
- Impact of Inflation and Deflation: Changes in COGS due to inflation or deflation can affect gross profit margins, making comparisons over time less reliable.
- Limited Financial Insight: It provides a snapshot of profitability but doesn’t account for cash flow, debt, or investments in assets.
While gross profit margin is a valuable metric, it has its limitations. If you want to check your business’ financial health, you need to check net profit margin through our free profit margin calculator.
Gross Profit Margin vs. Net Profit Margins and others
Gross profit margin differs from net profit margin and operating profit margin—two other key profitability ratios:
- Gross Profit Margin (GPM): Shows the percentage of revenue left after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS).
- It measures product or service profitability.
- Operating Profit Margin (OPM): Indicates the percentage of revenue left after subtracting operating expenses like rent, utilities, and salaries.
- It reflects the profitability of core business operations.
- Net Profit Margin (NPM): Represents the percentage of revenue remaining after all expenses, including taxes and interest, are deducted.
- It offers a complete view of overall profitability.
Each metric provides a unique perspective on profitability. Tracking all three helps you maintain a comprehensive view of your business’s financial well-being. Learn more about what to avoid when calculating profit for your Shopify store.
Understanding gross profit margin is critical to your store’s success. But calculating and tracking them manually? That’s time-consuming and prone to errors.
With TrueProfit, you can instantly access all your essential metrics in one place - no spreadsheets, no stress. Join thousands of Shopify merchants who have unlocked a clearer view of their net profit with our real-time profit tracking solution
Irene Le is the Content Manager at TrueProfit, specializing in crafting insightful, data-driven content to help eCommerce merchants scale profitably. With over 5 years of experience in content creation and growth strategy for the eCommerce industry, she is dedicated to producing high-value, actionable content that empowers merchants to make informed financial decisions.



 Shopify profits
Shopify profits