What Is Ecommerce Attribution: Models, Tips & Tools

eCommerce attribution is how you connect marketing efforts to actual sales and conversions. It tells you which ads, emails, and campaigns truly drive revenue.
The result? You stop wasting money on channels that don't work and double down on what actually drives profit.
In this guide, you'll learn exactly what attribution is, why it matters for scaling, the different attribution models available, and how to choose the right one for your store.
Let's dive in.
In this blog:
What is eCommerce Attribution?
eCommerce attribution is the process of identifying which marketing touchpoints lead to a sale or conversion.
Think of it as connecting the dots between your marketing efforts and sales.
Attribution tracks which marketing touchpoints lead to conversions.
Here's a real scenario:
Customer A sees your Facebook ad on Monday. He doesn't buy. On Wednesday, he clicks your Google ad and visits your site again. Still no purchase. Friday, she opens your email newsletter and finally buys.
The question: Which channel gets credit for the sale?
- Facebook (first touchpoint)?
- Google (middle touchpoint)?
- Email (final touchpoint)?
Attribution models answer this question. And getting it right is crucial for profitable scaling.
Why is Attribution Important for eCommerce?
Without proper attribution, you're flying blind.
Here's what happens:
You optimize the wrong channels. You see email drove the "last click" and pour all your money into email. But Facebook might have started the customer journey.
You waste ad spend. You turn off campaigns that seem ineffective but actually drive awareness and consideration.
You can't scale profitably. You don't know which channels truly drive profitable customers.
Proper attribution fixes this by:
- Optimizing marketing spend - Put money where it actually works
- Identifying high-performing channels - Double down on what drives results
- Reducing wasted ad spend - Stop funding channels that don't convert
- Informing scaling decisions - Know which campaigns to scale profitably
Types of eCommerce Attribution Models Explained
Each model tells a different story about your customer journey. Pick the wrong one and you'll optimize for the wrong channels.
Attribution Models: At-a-Glance Comparison
Here's how they stack up side by side:
Model | Credit Distribution | Best For | Sales Cycle | Setup Complexity | Data Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
First-Touch | 100% to first interaction | Brand awareness focus | 1-2 days | Simple | Minimal |
Last-Touch | 100% to final interaction | Conversion optimization | Same day | Simple | Minimal |
Linear | Equal credit to all touchpoints | Balanced channel view | 3-14 days | Easy | Low |
Time Decay | More credit to recent interactions | Performance marketing | 1-14 days | Medium | Medium |
U-Shaped | 40% first + 40% last + 20% middle | Awareness + conversion balance | 3-30 days | Medium | Medium |
W-Shaped | High credit to key milestones | Lead generation focus | 14+ days | Complex | High |
Data-Driven | ML determines credit distribution | Complex customer journeys | Any length | Very Complex | Very High |
1. First-Touch Attribution
First-touch attribution is a marketing attribution model that gives 100% of the credit for a conversion or sale to the very first marketing touchpoint a customer interacted with.
How it works:
- Customer sees Facebook ad (first touch).
- Later clicks Google ad.
- Finally converts via email.
Result: Facebook gets 100% credit.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Real example: Fashion brands see Facebook drives "80% of sales" via first-click attribution. But customers actually convert through email after seeing the Facebook ad. They overinvest in Facebook, underinvest in email optimization.
2. Last-Touch Attribution
Last-touch attribution is a marketing attribution model that gives 100% of the credit for a sale or conversion to the very last marketing touchpoint the customer interacted with before making a purchase.
How it works:
- Customer sees Facebook ad.
- Clicks Google ad later.
- Converts via email newsletter (last touch).
Result: Email gets 100% credit.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Real example: Supplement brand using last-touch sees "email drives 70% of sales." They cut Facebook ads. Sales drop 40% because Facebook was driving awareness that email converted.
Both last-touch attribution and last-click attribution focus on the final interaction, making them popular for direct response marketing optimization.
3. Linear Attribution
Linear attribution is a multi-touch attribution model that gives equal credit to every marketing touchpoint that a customer interacted with before making a purchase.
How it works:
The customer journey looks like this: Facebook ad → Google search → Email → Purchase
Linear attribution model will count: Each touchpoint gets 25% credit
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Real example: Beauty brand with customer journey spanning social media, influencer content, search ads, and email. Linear attribution shows each channel contributes equally, helping them maintain budget balance across all channels.
Linear attribution works well for businesses that want a balanced view of all marketing touchpoints without complex weighting systems.
4. Time Decay Attribution
Time decay attribution is a multi-touch attribution model that gives more credit to touchpoints that happened closer to the conversion, and less credit to those that occurred earlier in the customer journey.
How it works:
The customer journey over 7 days looks like this: Facebook ad (Day 1) → Google search (Day 5) → Email (Day 7) → Purchase
If you apply the time decay model: Facebook gets 20%, Google gets 35%, Email gets 45% of credit.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Real example: Electronics retailer with 5-day average consideration cycle. Time decay shows Google Shopping ads (day 4) and email (day 5) drive 70% of attribution, helping them optimize bid strategies for these high-impact, recent touchpoints.
Time decay attribution is particularly effective when considering the attribution window that defines how long after an interaction you'll credit it for a conversion.
4. U-Shaped (Position-Based) Attribution
U-shaped attribution (also called position-based attribution) is a multi-touch model that gives most of the credit to the first and last touchpoints, while splitting the remaining credit equally among any middle touchpoints.
How it works:
Customer journey: Facebook ad → Google search → Influencer post → Email → Purchase
Result: Facebook gets 40%, Google gets 10%, Influencer gets 10%, Email gets 40%
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Real example: Home goods brand with 2-week consideration cycle. U-shaped attribution shows Pinterest (awareness) and email (conversion) both deserve significant credit, preventing them from cutting Pinterest ads that drive initial product discovery.
The U shaped attribution model is ideal for businesses that want to balance investment in both awareness and conversion activities.
5. W-Shaped Attribution
W-shaped attribution is a multi-touch attribution model that expands on the U-shaped model by giving significant credit to three key milestones in the buyer’s journey:
How it works:
Customer journey: Facebook ad → Email signup → Google search → Email nurture → Purchase
And the final result is: Facebook gets 30%, Email signup gets 30%, Email nurture gets 30%, Google gets 10%
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Real example: Software subscription service tracks: ad view → free trial signup → email education → purchase. W-shaped gives credit to the ad (awareness), trial signup (lead conversion), and final email (purchase conversion).
The W shaped attribution model excels for businesses with clear lead generation funnels and multi-stage conversion processes.
6. Data-Driven Attribution
Data-driven attribution (DDA) is an advanced attribution model that uses your actual conversion data and machine learning to calculate how much credit each touchpoint truly deserves in the customer journey.
How it works: Algorithm analyzes thousands of customer journeys. Compares conversion rates with/without each touchpoint. Then assign credit based on actual influence on conversions
Real example: Large fashion retailer with 50,000+ monthly orders across 8+ channels. Data-driven attribution reveals YouTube ads have 3x more influence than expected, leading to 200% budget increase and 40% better overall ROAS.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Data-driven attribution represents the most sophisticated approach, using machine learning to understand your unique customer journey patterns.
How to Choose the Right eCommerce Attribution Model
Investing in the right marketing attribution software can make the difference between profitable growth and wasted ad spend.
Here are the 4 criteria to pick the right eCommerce attribution model:
- Your business size and data volume. Small stores under $1M with simple marketing don't need data-driven attribution. You don't have enough conversions for machine learning to work. And the complexity will slow down your decisions.
- Your sales cycle. Impulse purchases work perfectly with last-click attribution. But high-consideration products require multi-touch attribution to see the full influence chain.
- Your channel complexity. A $500K store running just Facebook ads can use last-click effectively. But a $2M store using Facebook, Google, email, influencers, and organic? You need U-shaped or linear attribution. When channels work together, single-touch models break completely.
- Your data quality. Inconsistent tracking, missing UTM parameters, and gaps in your customer journey mean sophisticated attribution models will give you sophisticated garbage.
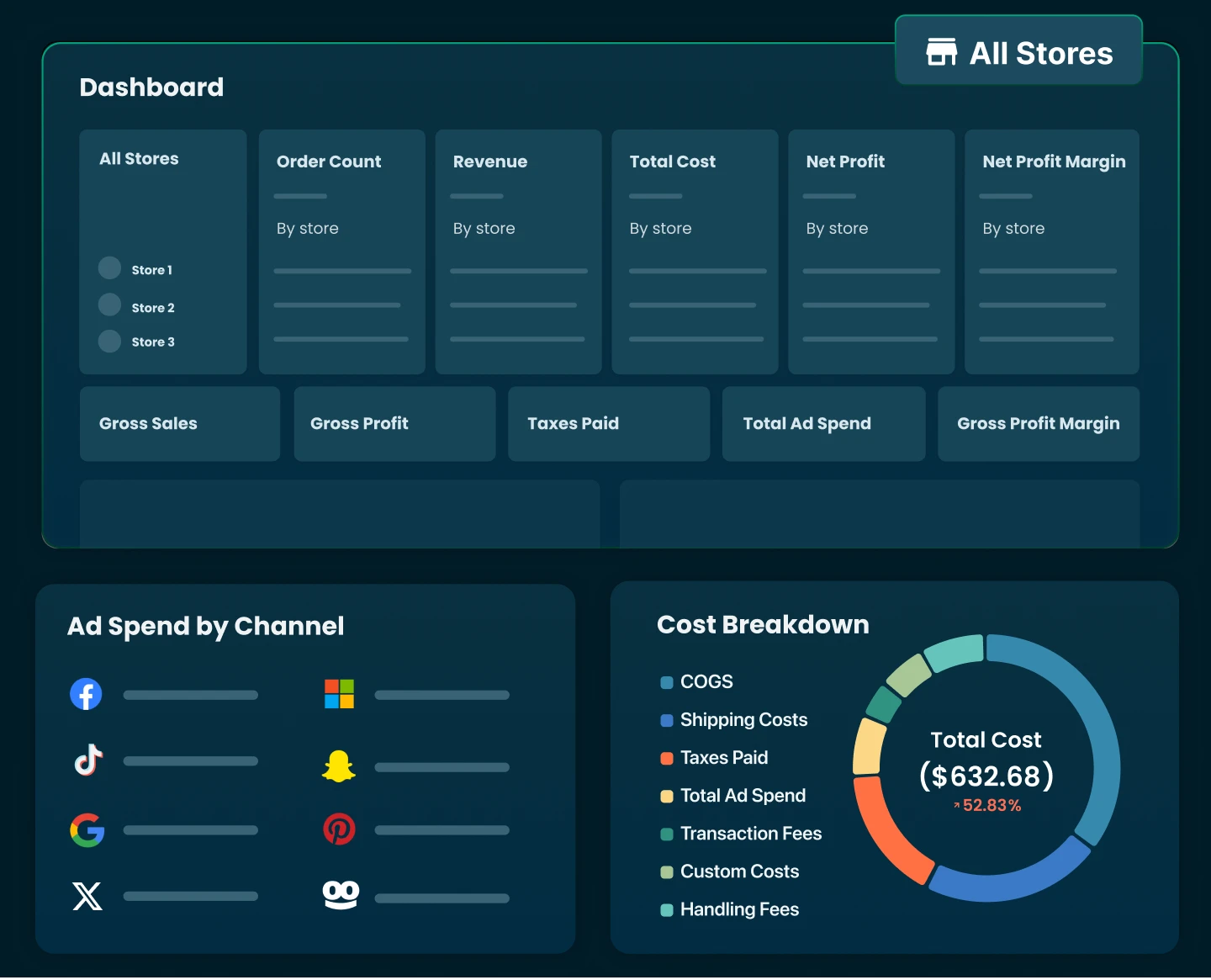
TrueProfit - Complete Customer Journey Attribution With Real Profit Tracking
Here's the problem with every attribution tool mentioned above:
- They track conversions, not profit.
- They died with iOS 14 and cookie limitations.
TrueProfit is a real-time net profit analytics platform built for Shopify sellers that solves this by combining marketing attribution with actual profit tracking. While other tools show which channels drive sales, TrueProfit shows which channels drive profitable sales.
Meanwhile, TrueProfit’s attribution model uses server-side tracking that works despite iOS privacy updates and cookie limitations that break most attribution tools.
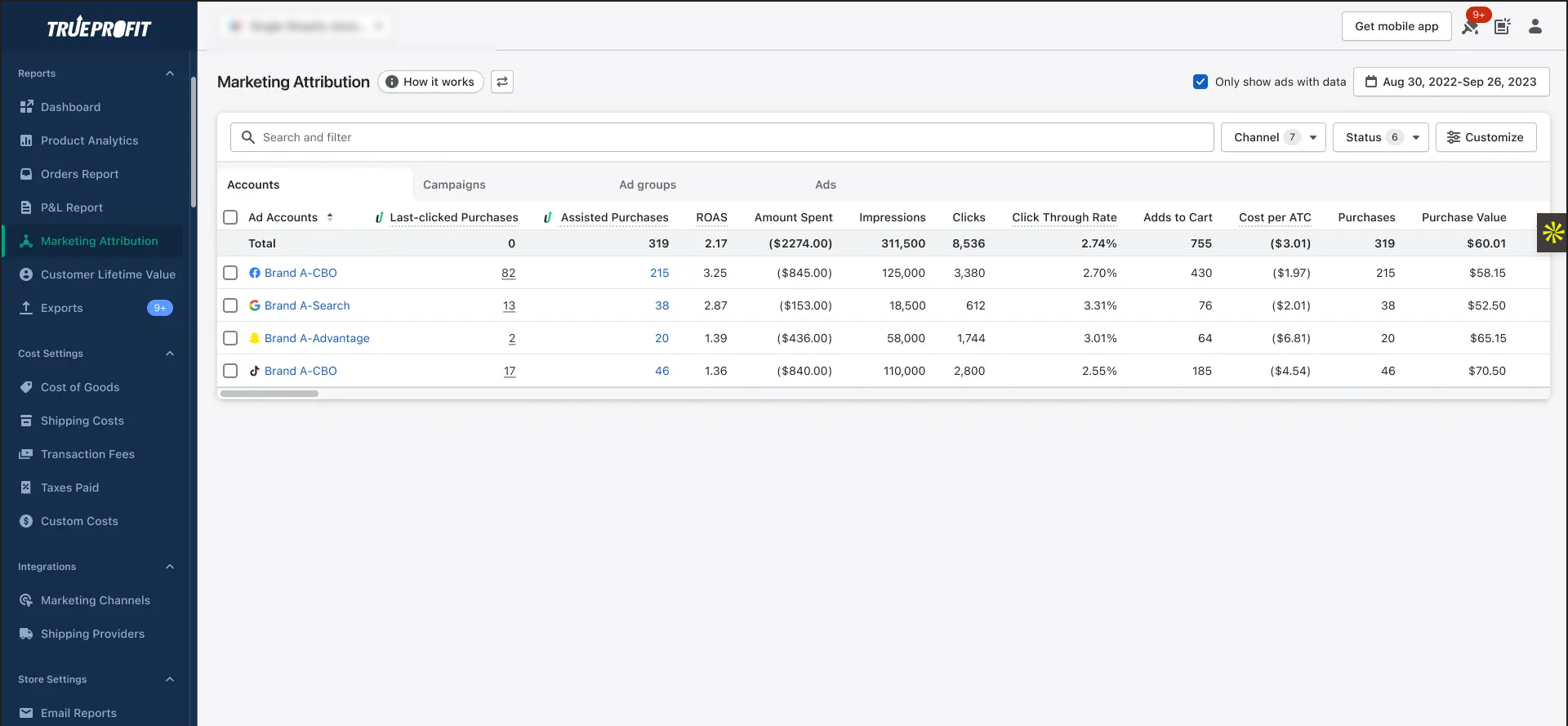
TrueProfit separates data into Assisted Purchases (top-funnel campaigns that introduce customers) and Last-Clicked Purchases (ads that directly drive conversions), giving you a complete picture of how channels work together.

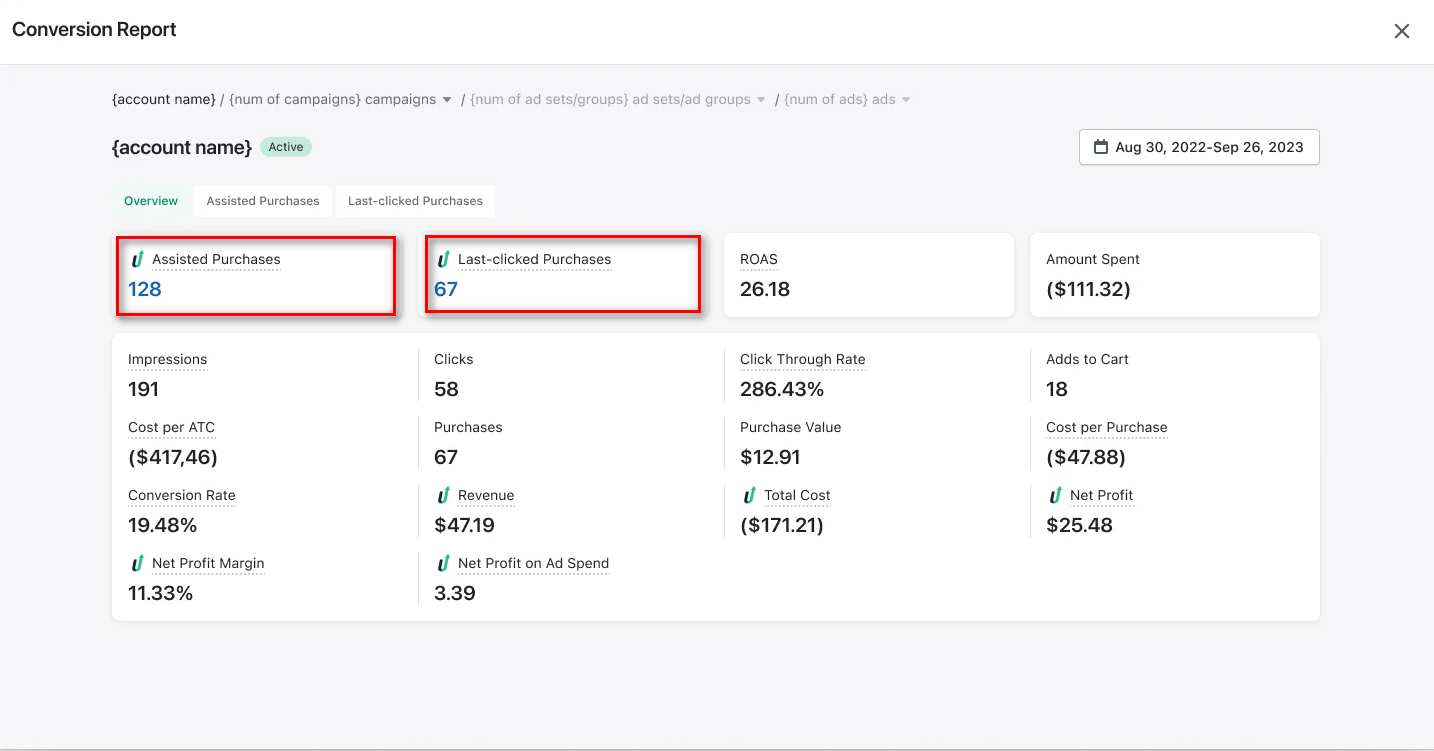
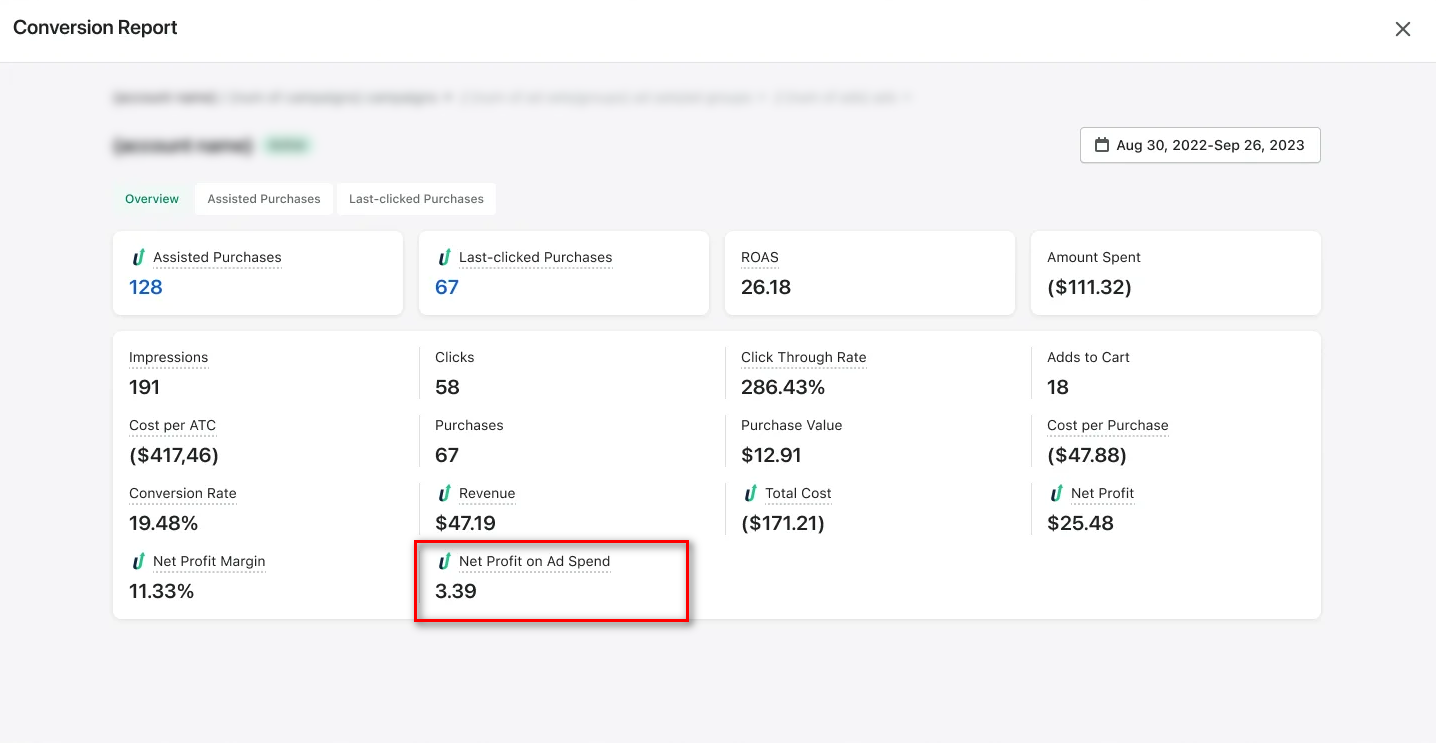
TrueProfit stands out because it focuses on Net Profit on Ad Spend instead of misleading ROAS metrics. You see actual profit after accounting for product costs, shipping, returns, and all expenses.
What’s even better? You can track this profit attribution at the campaign level, ad group level, or even individual ad level.
While other attribution tools guess at influence with broken tracking, TrueProfit measures actual profit impact with first-party data you can trust.
Irene Le is the Content Manager at TrueProfit, specializing in crafting insightful, data-driven content to help eCommerce merchants scale profitably. With over 5 years of experience in content creation and growth strategy for the eCommerce industry, she is dedicated to producing high-value, actionable content that empowers merchants to make informed financial decisions.


 Shopify profits
Shopify profits