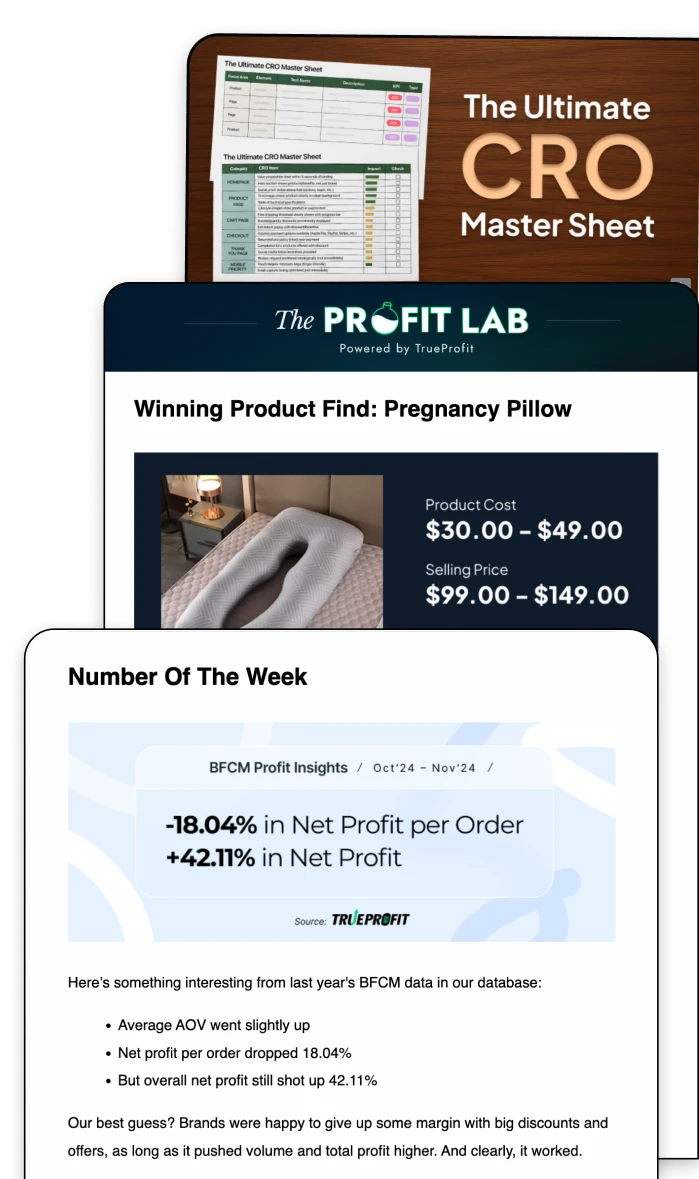
13 Essential Financial Performance Metrics Every Business Should Track (2026)

Financial performance metrics are key numbers that show how well your business is doing. They help you understand if you're making a profit, managing costs well, and how efficiently your business is running.
In this post, we’ll cover 13 essential financial metrics you should track to evaluate your business's financial health. We’ll show you how to use these metrics to make smarter decisions and drive growth. Whether you're new to business or a seasoned pro, understanding these metrics is crucial for success.
In this blog:
What Are Financial Performance Metrics?
Financial performance metrics are numbers that show how well your business is doing.
Financial performance metrics measure profit, efficiency, and growth. They give you a clear picture of your company’s financial health. Tracking these metrics helps you make better decisions, boost profits, and build a sustainable business.
Key Financial Performance Metrics to Track
Track the core metrics that reveal profitability, liquidity, efficiency, and leverage. These will give you a clear view of your business’s financial health.
Profitability Metrics
This one tells you how much money you’re actually keeping after covering the cost of making your product. The formula’s simple:
Why care? Because it shows whether your sales are doing more than just breaking even—they’re funding growth.
After all the bills are paid, what’s left? That’s your net profit margin. It’s the clearest signal of whether your business is financially healthy.
If this number’s low, your business might be working hard without much to show for it.
- Return on Equity (ROE)
This metric shows how well you’re turning investor money into actual profit.
Here’s the formula:
If ROE is high, it means you’re putting your investors’ money to good use. If it’s low, something might be dragging your business down.
Liquidity Metrics
- Working Capital
Can you cover your bills next month? That’s what this metric answers.
Take your Current Assets, subtract Current Liabilities, and you’ll see if your short-term finances are solid—or tight. Here’s the formula:
If you’ve got more assets than liabilities, your cash flow statement will typically show that you’re in a strong position to handle day-to-day expenses without breaking a sweat
- Quick Ratio
This is your “just in case” metric. If you can’t move your inventory, do you still have enough to pay the bills?
Formula:
It’s a solid way to test your liquidity without counting on sales.
Efficiency Metrics
- Return on Assets (ROA)
ROA tells you how good your business is at turning what it owns into real profit. It's like asking: “For every dollar in assets, how much income did we actually earn?”
To calculate it, divide your Net Income by your Total Assets.
The higher the number, the more efficiently you're putting your resources to work.
- Inventory Turnover
Think of this as your inventory’s pulse. It shows how often you sell and restock your products.
To figure it out, take your COGS and divide it by your Average Inventory.
A high turnover means your products don’t sit around long—great for keeping things liquid.
- Accounts Receivable Turnover
This tells you how quickly your customers are paying their invoices. The faster they pay, the better your cash position.
To calculate it, take your Net Credit Sales and divide by your Average Accounts Receivable.
A high turnover means your collection process is working. A low one? Might be time to chase those unpaid bills.
- Accounts Payable Turnover
It tells you how often you pay your suppliers. A higher number means quicker payments. A lower one may point to cash flow problems.
To figure it out, divide COGS by Average Accounts Payable.
The higher the turnover, the better you’re managing cash outflows.
Leverage Metrics
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio
This ratio compares the amount of debt you have to the amount of equity in your business. A high ratio means you're borrowing a lot, which could be risky if things go wrong.
You find it by dividing your Total Debt by Shareholders’ Equity.
A low ratio means you’re using less debt to fund your business, which often means lower risk.
- Interest Coverage Ratio
This metric tells you if you’re in a good position to pay the interest on your debt. A higher ratio means you’re managing debt better, while a lower one could indicate trouble.
To calculate it, divide EBIT by Interest Expense.
Think of it as your ability to cover the cost of borrowing. The higher the ratio, the more secure you are.
eCommerce Essential Metrics
Here’s the deal: CAC tells you how much you’re spending to get each new customer. A high CAC could be a red flag if it’s eating into your profits.
It’s calculated by dividing your Total Marketing Spend by your New Customers Acquired.
To keep things healthy, make sure this number stays reasonable compared to the value each customer brings.
CLV helps you estimate the total revenue a customer will bring over their lifetime. A higher CLV means you're building strong, repeat relationships with customers, which is key to sustainable growth.
You calculate it by multiplying Average Order Value, Purchase Frequency, and Customer Lifespan.
It’s one of the best ways to measure long-term profitability per customer.
For more ecommerce-specific metrics, check out these 15+ essential ecommerce metrics every store should track.
Tracking these 13 metrics gives you a rounded view of profit, cash health, operational efficiency, and financial risk—enabling smarter decisions and sustainable growth.
Is Financial Performance Metric a KPI?
Financial business performance metrics can serve as KPIs when they align with your business goals. KPIs are specific, measurable indicators that show how well you’re achieving key objectives.
What Are KPIs?
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are numbers you track to measure success. They help you see if your strategies are working.
Financial Metrics as KPIs
- Net Profit Margin: Tracks profitability. Use it as a KPI to ensure you meet profit targets.
- Return on Assets (ROA): Measures asset efficiency. As a KPI, it shows if you’re using resources well.
- Operating Cash Flow: Monitors cash health. Use it to confirm you have enough cash for operations.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): In eCommerce, these metrics are vital KPIs. They help you balance marketing spend with long-term revenue.
By choosing the right financial metrics as KPIs, you can focus on what truly drives your business forward.
How to Evaluate Financial Performance
To evaluate financial performance, focus on the few metrics that tie directly to your goals—profitability, cash health, or growth—and compare them against targets or benchmarks.
Step 1: Identifying focused metrics
- Profitability goals: Track Net Profit Margin and Gross Profit Margin to see if you’re making the profits you need.
- Cash‐flow stability: Monitor Operating Cash Flow and Quick Ratio to ensure you can cover bills and invest in growth.
- Efficiency goals: Use Return on Assets (ROA) and Inventory Turnover to check how well you use resources.
Step 2: Analyze metrics
- Set benchmarks: Compare each metric to industry averages or your own past performance.
- Identify gaps: If a metric falls short, drill into the underlying numbers (e.g., high COGS reducing gross margin).
- Trend analysis: Track metrics over time to spot improving or declining patterns rather than relying on a single snapshot.
By focusing on the metrics that map to your strategic goals, comparing them to benchmarks, and adjusting for eCommerce specifics, you can clearly assess financial health and take targeted actions.
From Financial Performance Metrics to Practical Insights
- Optimize Ad Spend
- Compare ROAS (return on ad spend) to CAC. Cut underperforming channels.
- Compare ROAS (return on ad spend) to CAC. Cut underperforming channels.
- Adjust Pricing
- Use Gross Profit Margin data to set prices that cover costs and leave room for profit.
- Use Gross Profit Margin data to set prices that cover costs and leave room for profit.
- Manage Inventory
- Slow-moving items: run promotions to boost Inventory Turnover.
- Fast-moving items: ensure adequate stock to avoid stockouts.
- Slow-moving items: run promotions to boost Inventory Turnover.
- Improve Customer Retention
- Track CLV trends. Launch loyalty programs if CLV falls below target.
- Track CLV trends. Launch loyalty programs if CLV falls below target.
By applying these metrics, eCommerce businesses can make data-driven choices that boost profitability, improve cash flow, and support sustainable growth.
Financial performance metrics help you see the full picture of your business health. The biggest takeaway? Don’t just track revenue — track what actually drives profitability, efficiency, and growth.
Knowing these 13 essential metrics gives you clarity. It helps you spot issues early and make better decisions. Start simple, stay consistent, and let the numbers guide your next move.
Harry Chu is the Founder of TrueProfit, a net profit tracking solution designed to help Shopify merchants gain real-time insights into their actual profits. With 11+ years of experience in eCommerce and technology, his expertise in profit analytics, cost tracking, and data-driven decision-making has made him a trusted voice for thousands of Shopify merchants.


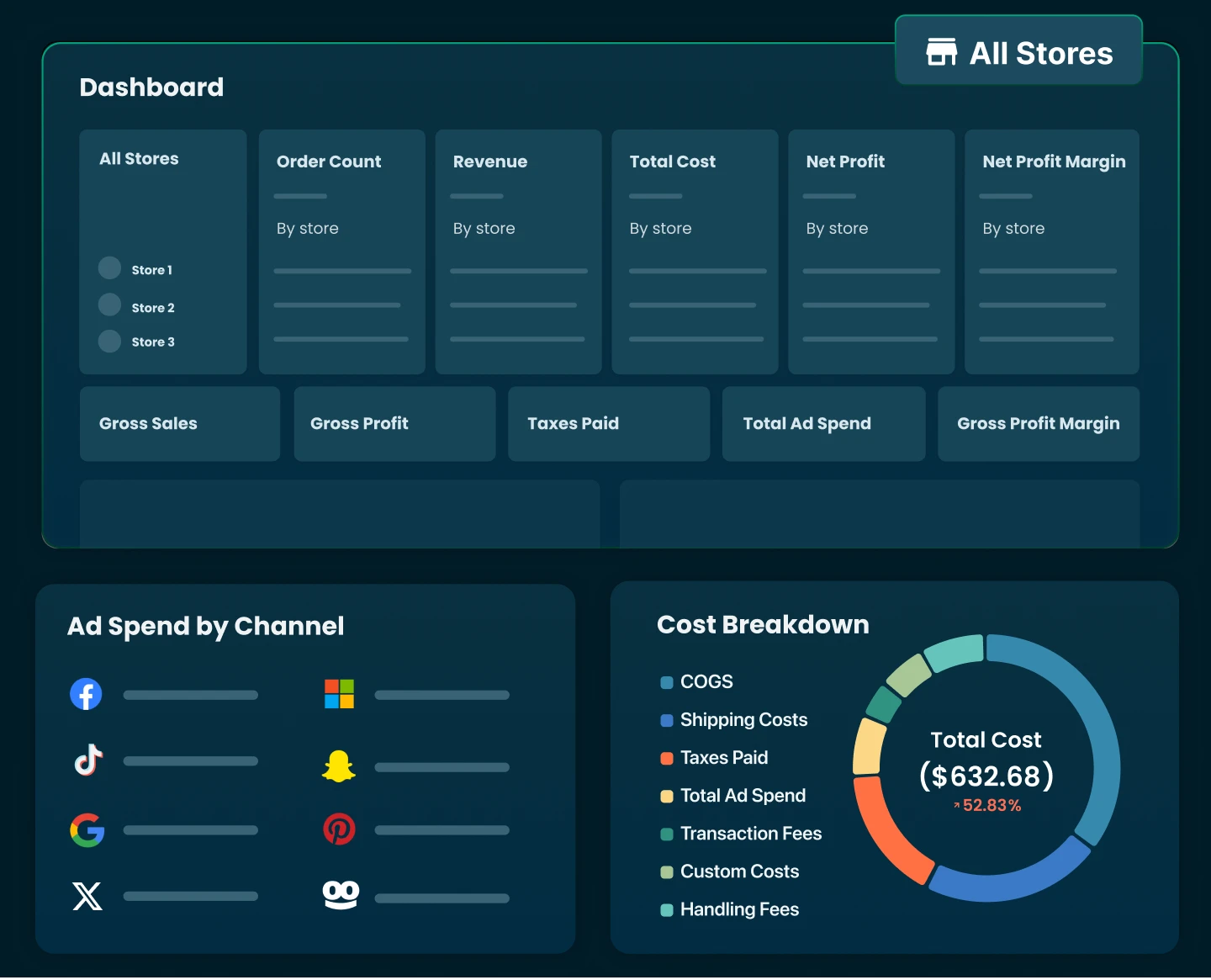
 Shopify profits
Shopify profits