Profit and Loss vs. Balance Sheet (Differences + Examples)

A Profit and Loss statement shows how much profit or loss a business has made over a specific period, focusing on revenues and expenses. On the other hand, a Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a single point in time, detailing assets, liabilities, and equity.
In this article, we’ll break down the differences between profit and loss vs balance sheet, offer clear examples, and explain when and how to use each to manage your business finances effectively.
In this blog:
What is the Difference between a P&L and Balance Sheet?
Feature | Profit and Loss Statement | Balance Sheet |
|---|---|---|
Purpose | Measures performance over time | Shows financial position |
Timeframe | Covers a specific period | Snapshot at a specific date |
Key Metrics | Revenue, expenses, net profit | Assets, liabilities, equity |
Common Use Case | - Assess profitability: Check if the business is making more money than it’s spending. | - Evaluate stability: Check if the business is financially stable long-term. |
Frequency | Monthly, quarterly, annually | Often prepared quarterly/yearly |
When to Use Each Statement?
- Use a Profit and Loss Statement when evaluating whether your business is profitable, where expenses can be trimmed, or to prepare for tax filing.
- Use a Balance Sheet when applying for loans, gauging your company's stability, or assessing your ability to pay off debts.
Together, these statements help tell the full story of your business’s financial health.
What is a Profit and Loss Statement?
A Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement, also known as an income statement, shows your business’s financial performance over a period of time—typically monthly, quarterly, or yearly. It tracks how much revenue you’ve earned and subtracts all your costs and expenses to reveal your net profit (or loss).
For e-commerce businesses, the P&L statement is like your scoreboard. It shows whether your store is actually making money or bleeding cash.
Key components of P&L statement:
- Revenue (Sales): This is the total income from product sales, including Shopify sales, marketplace orders, and any other channels.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): What you paid to produce or purchase the products you sold—including dropshipping supplier costs, packaging, and shipping fees.
- Operating Expenses: These cover everything from marketing (Facebook Ads, influencers), subscription tools (Shopify apps, email platforms), to salaries and fulfillment services.
- Net Profit (or Loss): What’s left after all expenses—this is the number that shows if your business is financially healthy.
Example of P&L statement: Let’s say you run an online apparel store. In Q1, your total revenue was $50,000. Your COGS was $20,000, and your operating expenses totaled $15,000. Your net profit would be:
$50,000 (Revenue) - $20,000 (COGS) - $15,000 (Expenses) = $15,000 Net Profit
If you're looking for a simpler way to know your profit and loss instantly, try this free profit calculator.
Why Profit and Loss Statement Matters for E-commerce:
- Track real-time performance – See if your recent campaigns or product launches are actually profitable.
- Set smarter budgets – Know exactly how much you can spend on ads, tools, or new hires without going negative.
- Make tax time easier – A well-organized P&L makes it easier to file taxes and claim accurate deductions.
- Optimize margins – Identify hidden costs and find where you’re leaking money like overspending on ad platforms or poor SKU performance.
What is a Balance Sheet?
A Balance Sheet is a financial statement that shows a business’s financial position at a specific point in time. It summarizes what the business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the owner’s equity - the remaining value after liabilities are subtracted from assets.
For e-commerce businesses, the balance sheet plays a critical role in understanding your store’s financial health beyond just sales.
Key Components of Balance Sheet:
- Assets include your inventory, cash in the bank, equipment (like computers or photography gear), and accounts receivable (unpaid customer invoices). For dropshippers, this may lean more toward digital assets or receivables.
- Liabilities cover outstanding supplier payments, loans, credit card debts, or any other money the business owes.
- Owner’s Equity reflects how much the business is truly worth to the owner after paying off all debts. It's essentially your stake in the business.
The formula is:
Example of Balance Sheet: Let’s say your online store has:
- $10,000 in cash
- $5,000 in inventory
- $3,000 in outstanding customer payments (accounts receivable)
- $6,000 in credit card debt
- $2,000 loan balance
Your equity would be:
$10,000 + $5,000 + $3,000 = $18,000 (Assets)
$6,000 + $2,000 = $8,000 (Liabilities)
$18,000 - $8,000 = $10,000 (Equity)
Why Balance Sheet Matters for E-commerce:
- Gauge your ability to scale – If you’re looking to invest in ads, new SKUs, or team members, your balance sheet will show whether you can afford it.
- Secure funding – Lenders and investors often look at your balance sheet to assess if your business is stable enough to support additional investment.
- Track business health over time – By comparing balance sheets from different periods, you can spot trends in growth, cash flow, and liabilities.
Best Tools for Managing Financial Statements
If managing finances manually feels overwhelming, you're not alone. Many business owners rely on tools to streamline the process. Here are a few profit and loss app:
- TrueProfit – Automatically tracks your profit and loss in real-time, including store profit, ad spend, product costs, and more.
- Excel or Google Sheets – Good for beginners but very prone to errors.
Knowing the difference between profit and loss vs balance sheet is key - but manually tracking it all isn’t scalable.
TrueProfit is an advanced profit tracker that gives Shopify store owners real-time, accurate, and automated profit tracking. It cuts through data clutter and delivers net profit-focused insights so you can track what truly matters - your bottom line.
Harry Chu is the Founder of TrueProfit, a net profit tracking solution designed to help Shopify merchants gain real-time insights into their actual profits. With 11+ years of experience in eCommerce and technology, his expertise in profit analytics, cost tracking, and data-driven decision-making has made him a trusted voice for thousands of Shopify merchants.



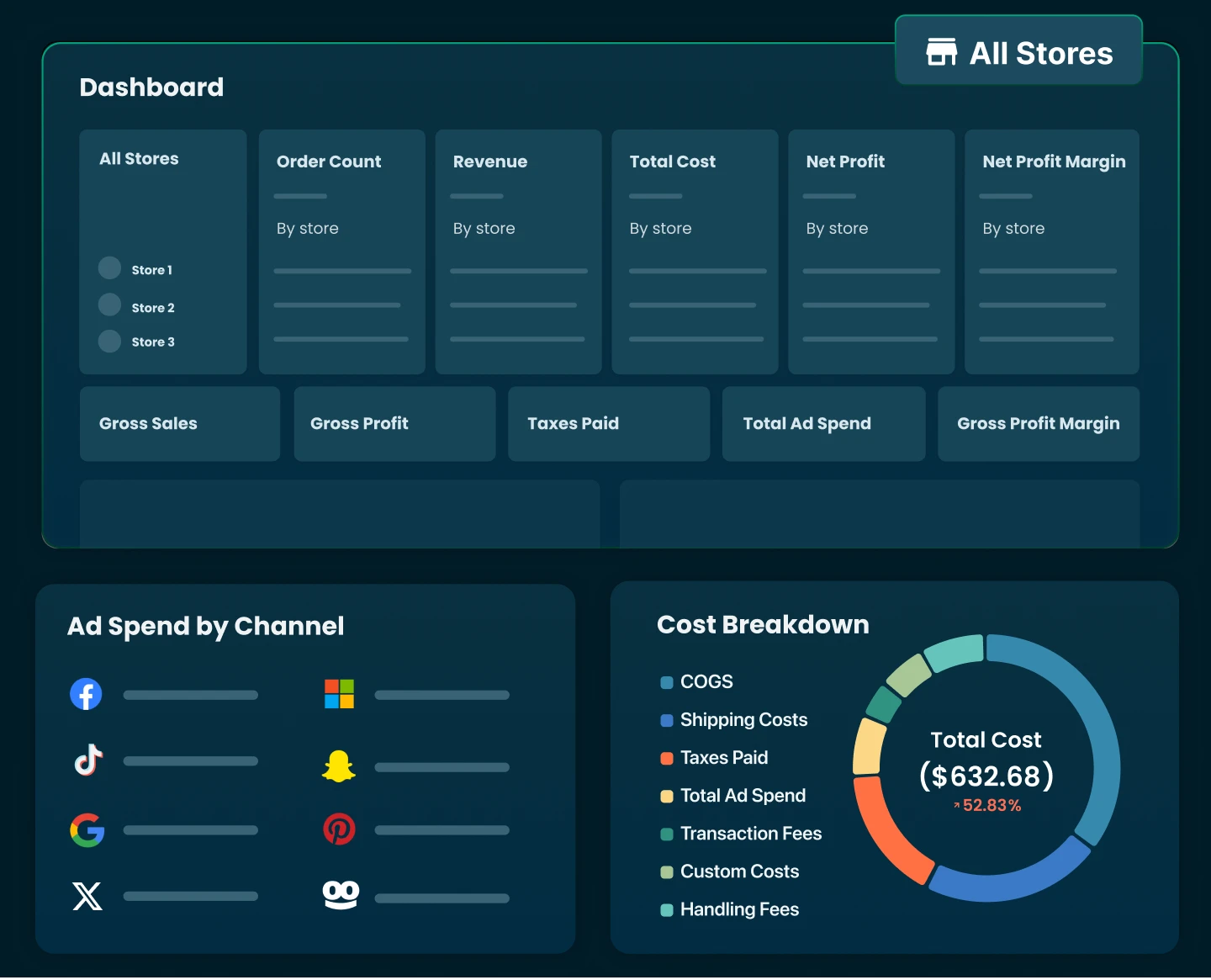
 Shopify profits
Shopify profits