How to Calculate Profit Per Unit (With Examples & Formulas)
Knowing how many units you sell is easy. But knowing how much you actually make on each unit is what separates profitable businesses from busy ones.
That’s where profit per unit comes in.
In this guide, we’ll break down what profit per unit really means, how to calculate it step by step, and how it fits into other core profit formulas used in eCommerce.
In this blog:
What Is Profit Per Unit?
1. Definition
Profit per unit (also called profit per product) is the amount of profit you earn from selling one unit of a product.
In its simplest form:
This metric answers a very direct question: “Every time I sell this product, how much money do I actually keep?”
Unlike revenue or order count, profit per unit focuses on quality of sales, not just sales volume.
2. Types of Profit Per Unit
One reason profit per unit is often confusing is that people use it to mean different things.
There are two common interpretations:
Type 1: Gross Profit Per Unit
Gross profit per unit only considers costs directly tied to producing or sourcing the product or we also known as COGS.
COGS typically includes:
- Product or manufacturing cost
- Supplier cost
- Basic fulfillment or packaging
This version is useful for comparing products at a high level, but it ignores many other real expenses.
Type 2: Net Profit Per Unit (Most Practical)
Net profit per unit subtracts all costs associated with selling one unit.
Total cost per unit may include:
- Product cost (COGS)
- Shipping & fulfillment
- Payment processing & platform fees
- Advertising cost per conversion
- Refunds, returns, disputes (averaged per unit)
In practice, when business owners talk about profit per unit, they usually mean net profit per unit, because it reflects reality.
In this article, we’ll primarily use that approach, but we’ll always make the distinction clear.
How to Calculate Profit Per Unit (Step by Step Guide)
The formula itself is simple:
The real challenge is calculating cost per unit correctly.
Step 1: Identify Your Selling Price Per Unit
This is the amount the customer pays at checkout (before refunds).
Example:
- Selling price = $50
Step 2: Calculate Total Cost Per Unit
This is where many sellers go wrong.
A realistic cost per unit often includes:
- Product or supplier cost
- Shipping & fulfillment
- Transaction fees (Shopify, PayPal, Stripe, etc.)
- Advertising cost per sale (CPA)
- Refunds or disputes (averaged over time)
For example:
- Product cost: $22
- Shipping & fulfillment: $5
- Transaction fees: $2
- Ads per conversion: $6
Then your total cost per unit is $35.
Step 3: Apply the Formula
At this point, you just apply the formula and the final result is:
Profit per unit = $50 − $35 = $15
That means every sale puts $15 of real profit into your business.
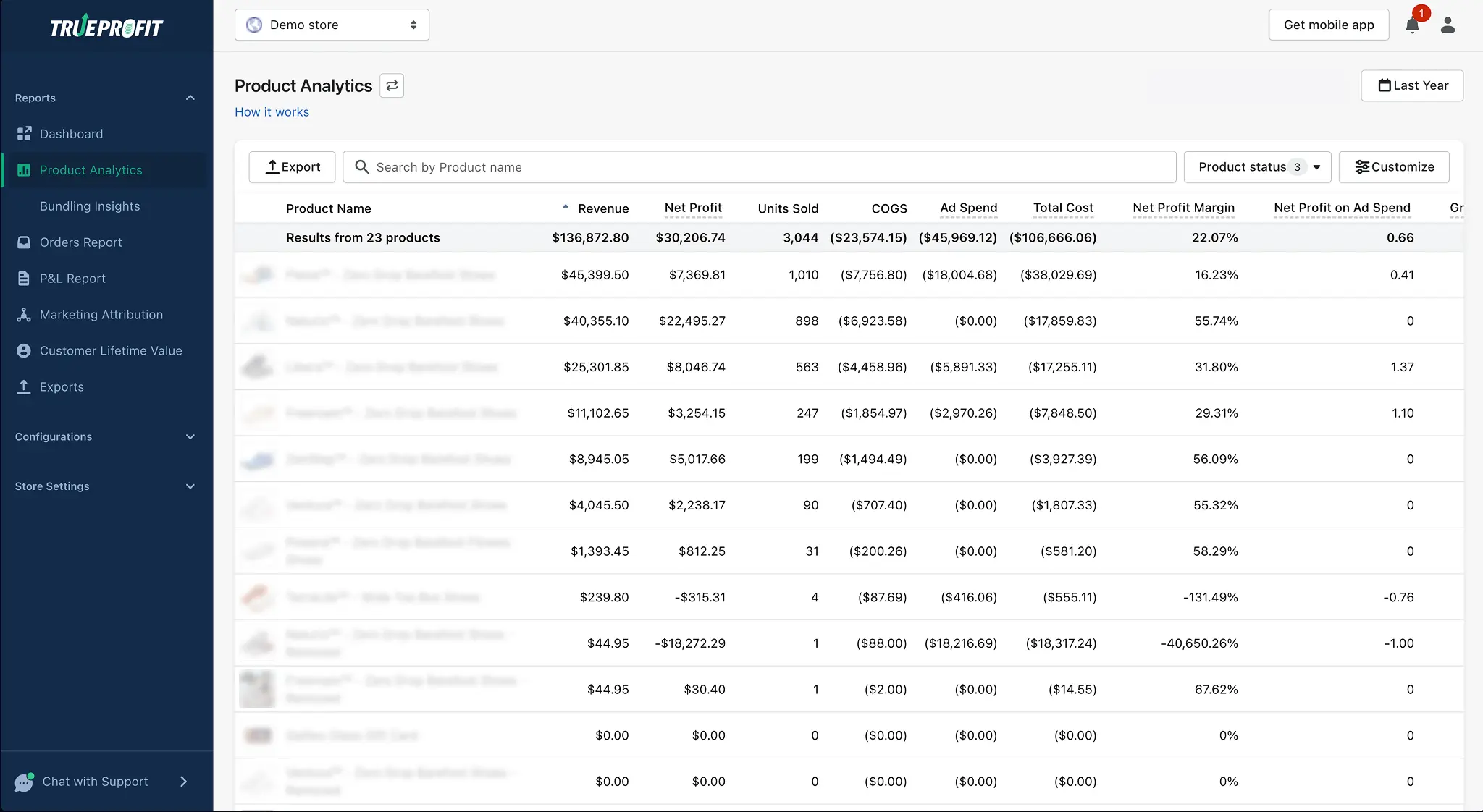
Why Tracking Profit Per Unit Is Important for Ecom Business?
Whether you’re testing a new product or scaling your best-sellers, knowing how to calculate profit per unit or profit margin per unit ensures you’re not just moving inventory—you’re actually making money with every sale.
Many merchants make the mistake of focusing only on revenue or order volume. But if you don’t know exactly how much profit you earn per product sold, it’s easy to fall into common traps: pricing too low, overspending on ads, or scaling a product that’s actually draining your margins.
Here’s why this metric is a must-have in your toolkit:
- Set profitable prices (without guesswork): Know your break-even point, margin buffer, and how much room you have to discount while still staying in the green.
- Catch low-margin products early: Not every best-seller is profitable. This metric lets you flag products with strong sales but weak returns before they eat into your bottom line.
- Plan smarter promotions: Want to offer 20% off or free shipping? Knowing your per-unit profit lets you calculate how far you can go without turning a win into a loss.
- Compare product performance fast: You’ll quickly see which SKUs are worth scaling and which ones deserve a quiet retirement.
Keep Track of Your Profit Per Unit from Day One
Profit per unit may look like a simple formula, but it’s one of the most revealing metrics in eCommerce.
It forces you to stop guessing and start answering hard questions:
- Which products actually make money?
- How much can you afford to spend to acquire a customer?
- Is growth helping or hurting your business?
The challenge isn’t the math. It’s keeping the numbers accurate and up to date as costs change.
That’s why many Shopify merchants rely on profit tracking tools like TrueProfit that automatically calculate profit per unit, gross profit, and net profit in real time so decisions are based on reality, not assumptions.
Tracy is a senior content executive at TrueProfit – specializing in helping eCommerce businesses scale profitably through content. She has over 4 years of experience in eCommerce and digital marketing editorial writing. She develops high-impact content that helps thousands of Shopify merchants make data-driven, profit-focused decisions.


 Shopify profits
Shopify profits