What Is Gross Profit And How To Calculate It?

Gross profit is the amount of profit remaining from total sales after subtracting the direct costs of producing or purchasing the goods it sold.
These direct costs are known as the cost of goods sold (COGS) and typically include expenses such as materials and direct labor used in production. It does not include operating expenses like rent, utilities, marketing, or administrative costs.
The formula for calculating gross profit is:
In this guide, you’ll learn what gross profit is and how to calculate it. We’ll also provide you with simple examples to make it clear.
In this blog:
What is Gross Profit?


Gross profit is the revenue that remains after subtracting the direct costs of purchasing or producing the products sold (Cost of goods sold).
Cost of Goods Sold typically includes:
- Product purchase cost or manufacturing expenses
- Shipping costs from suppliers to your warehouse
- Import duties and customs fees
- Packaging materials for customer orders
- Payment processing fees
- Direct labor costs for product preparation
Gross profit reflects the profitability of your products and sales before accounting for operating expenses.
Stores use it as an early indicator for their product profitability. Without it, you can’t see if your products are truly profitable. Tracking it shows whether your pricing and sourcing decisions are boosting your bottom line.
How to Calculate Gross Profit for eCommerce Stores?
Gross profit is calculated using this formula:
Let’s say your store made $20,000 in sales this month. Your COGS included:
- Product costs: $9,000
- Shipping from suppliers: $1,000
- Packaging: $500
- Payment processing fees: $300
Your total COGS = $9,000 + $1,000 + $500 + $300 = $10,800.
Using the formula: Gross Profit = $20,000 – $10,800 = $9,200
So in this example, your gross profit of $9,200 shows the amount your store retains from sales after paying for product and shipping costs. It helps you see if your pricing strategy and products are generating profit before you factor in other business expenses.
What is a Good Gross Profit Margin?
A good gross profit margin varies significantly by product niche and business model. That’s why high-profit-margin businesses can have different profit margins, but they all land in a healthy range.
- Excellent (50%+): Digital products, software, high-end specialized items
- Good (30-50%): Branded products, niche markets, premium positioning
- Average (20-30%): General retail, competitive markets, commodity products
- Challenging (Under 20%): Highly competitive markets, low-margin products
As Harry Chu - Founder of TrueProfit notes, "A newer eCommerce business might accept lower margins initially to attract customers, while established businesses should focus on optimizing margins for long-term profitability."
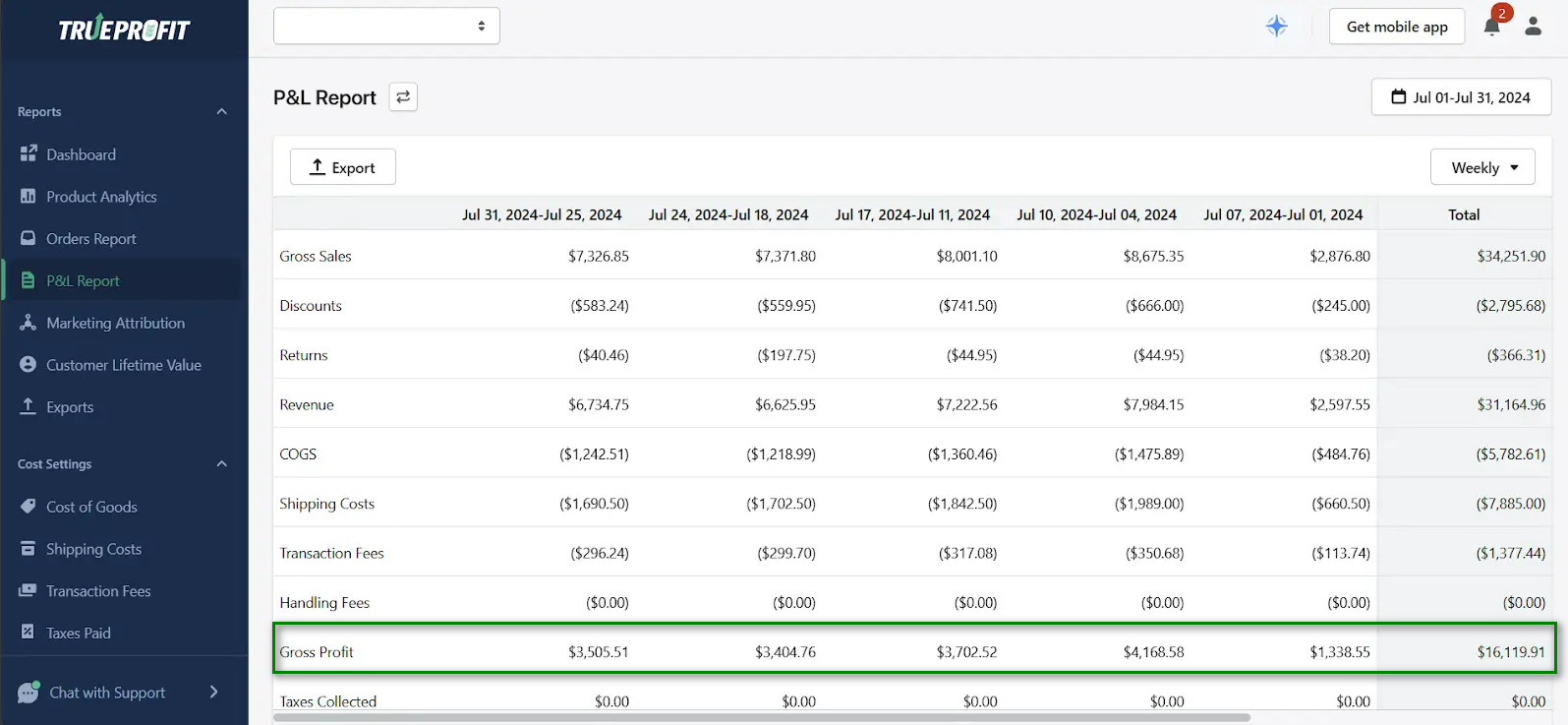
How to Find Gross Profit on PnL Report?
In your Profit and Loss report, gross profit appears as the first major profitability indicator. Here's how it typically looks:

8 Best Practices to Improve Gross Profit
8 smart, multi-step approaches to improve your gross profit in 2025:
1. Start by focusing on your product mix.
Track which products bring the highest margins and push those harder.
At the same time, review low-margin products that don’t move enough volume—consider adjusting their price or removing them.
2. Leverage your growth to negotiate better supplier terms.
Use your buying power to secure lower costs, better payment conditions, and reduced shipping fees.
Working with multiple suppliers keeps pricing competitive and your margins healthy.
3. Adjust pricing based on order history data.
Use data-backed methods like dynamic pricing, competitor analysis, and value-based pricing.
Test price increases carefully on high-demand products where competition is low to protect sales volume while boosting margins.
4. Cut rate of return even before checkout.
Cut rate of return by improving product descriptions, offering accurate size guides, and using high-quality images.
Collect and highlight customer reviews to build trust, and keep strict quality control to avoid defective products.
5. Prove you worth cheaper COGS
Negotiate carrier rates, optimize packaging to avoid dimensional weight fees, and consider multiple fulfillment centers to cut shipping rates.
6. Product bundling helps too.
Bundles increase average order value and can boost overall margins while helping clear slower-moving stock.
7. Focus on retention.
Repeat customers usually buy higher-margin products and cost less to acquire.
That means better gross profit over time.
8. Monitor these efforts with detailed metrics.
When you connect the dots between pricing, product mix, returns, and shipping, you gain the insights needed to steadily grow your gross profit and build a sustainable business.
Understanding gross profit is essential for making smart business decisions but tracking it manually can be a hassle. That’s where TrueProfit comes in.
It automatically pulls in your costs, including COGS, ad spend, shipping, and more, giving you real-time insight into your actual profit. No spreadsheets, no guesswork. Just clear, accurate data whenever you need it.
Whether you’re scaling or just starting out, knowing your true numbers is key. TrueProfit helps you stay on top of your margins so you can grow confidently. Start tracking your gross profit the easy way with TrueProfit.
Leah Tran is a Content Specialist at TrueProfit, where she crafts SEO-driven and data-backed content to help eCommerce merchants understand their true profitability. With a strong background in content writing, research, and editorial content, she focuses on making complex financial and business concepts clear, engaging, and actionable for Shopify merchants.








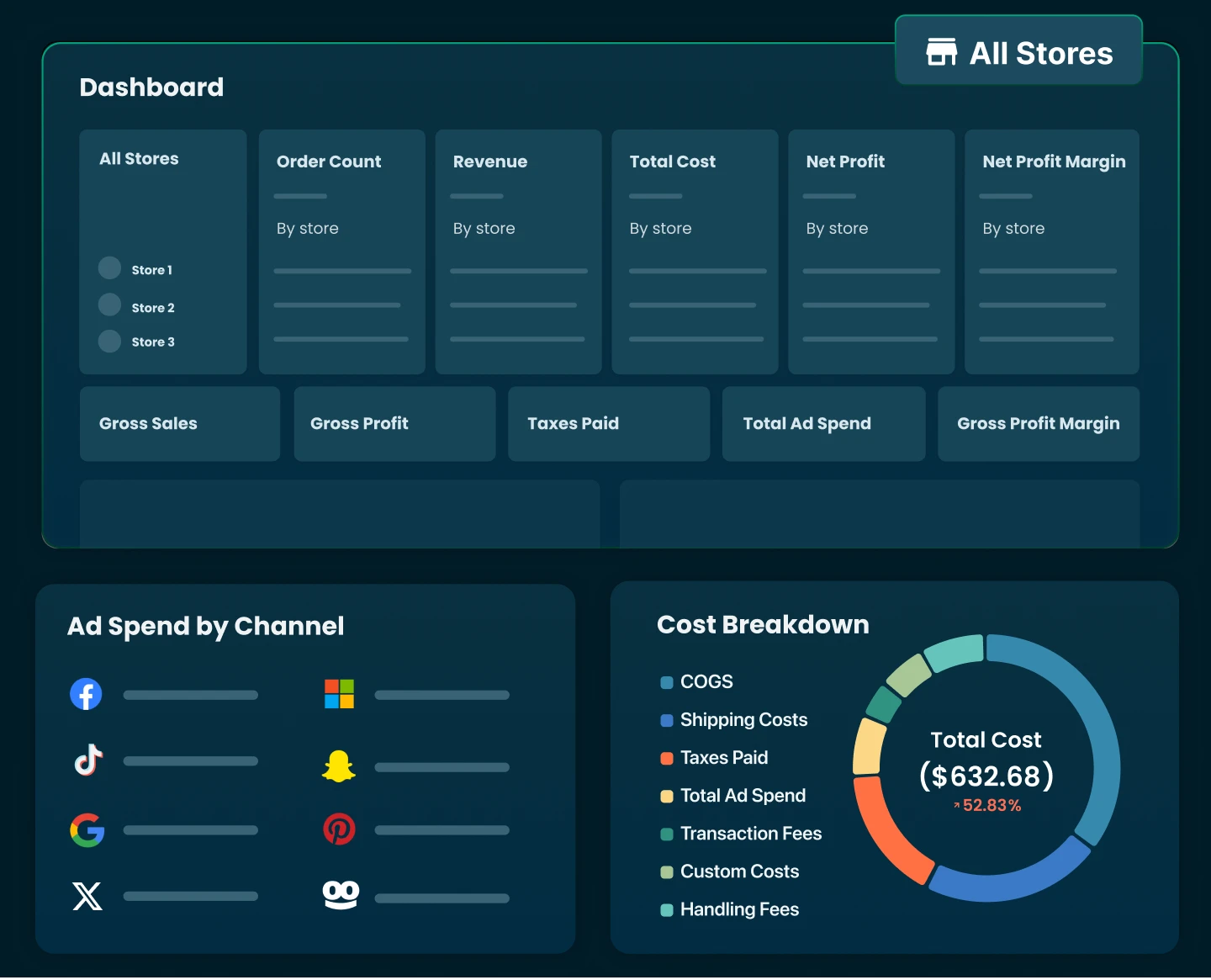
 Shopify profits
Shopify profits