What Is A Good Operating Profit Margin? The 2025 Answer
Operating profit margin measures how much profit a business keeps from its revenue after covering all operating expenses (like COGS, ads, salaries, and tools), but before interest and taxes. It shows how efficiently the core business operates.
In this guide, we’ll break down what defines a good operating margin, what affects it, how it varies by industry, how to calculate it and why it’s one of the most important numbers for running a healthy business.
Quick Recap:
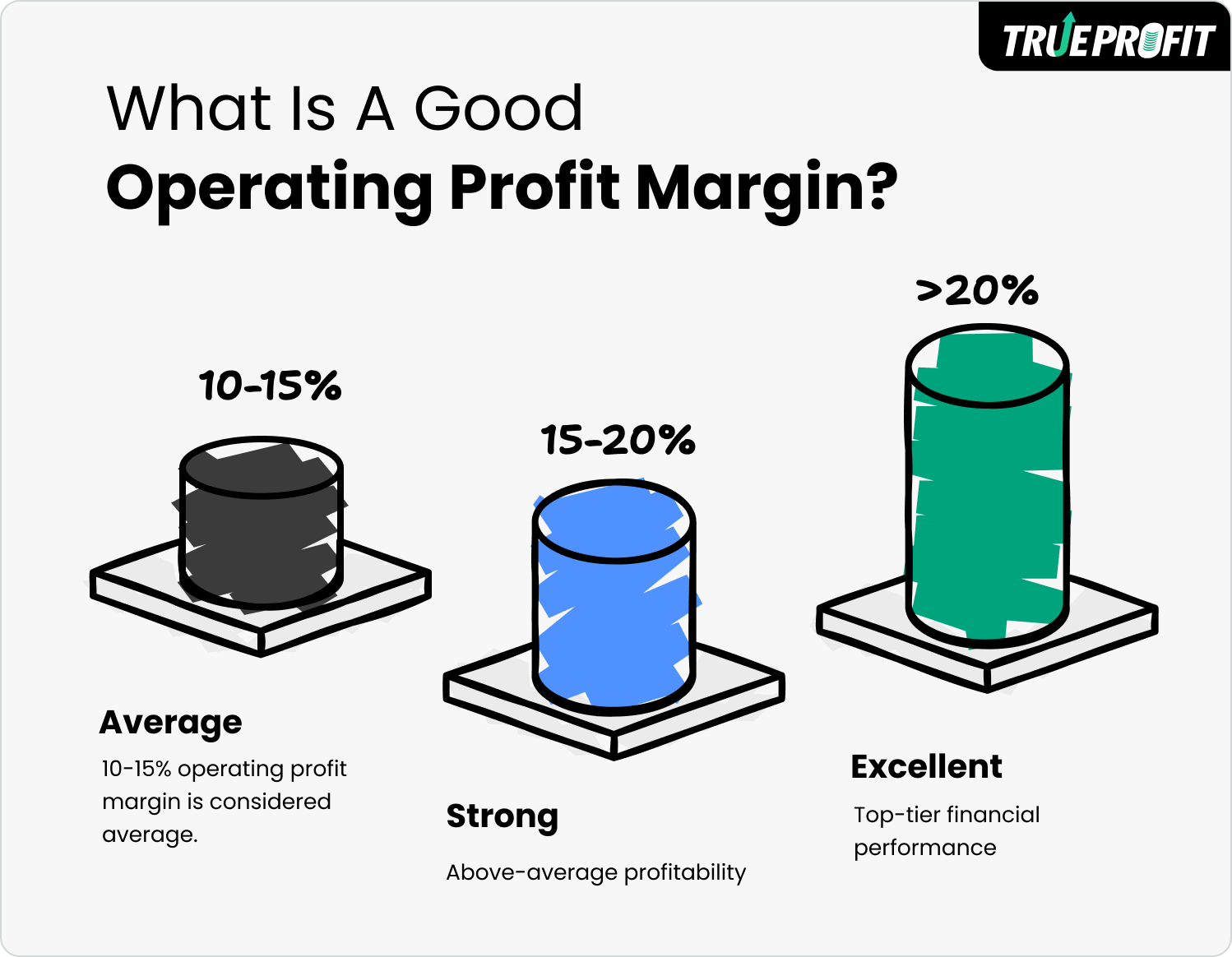
- A 10-15% operating profit margin is considered good. 15–20% is strong, and anything beyond is excellent.
- There isn't a one-size-fits-all margin. What’s considered a “good” margin in retail might be disappointing in tech.
- What matters more is that your margin is stable or improving over time. A margin that’s improving quarter over quarter is often a stronger signal than one impressive spike.
In this blog:
What Is a Good Operating Profit Margin?
Generally speaking, a 10-15% operating profit margin is considered average. 15–20% is strong, and anything beyond is excellent.
But there’s no one-size-fits-all “ideal” margin—it varies by industry.
For instance, a SaaS company with low overhead might regularly hit margins over 20%, while a retail brand may sit closer to 5–10% due to higher costs.
Operating Profit Margin Benchmark by Industries
Here's a breakdown of average operating profit percentage across major industries:
Consumer Goods & Retail
- Apparel: 8.73%
- Furn/Home Furnishings: 6.51%
- Household Products: 18.38%
- Office Equipment & Services: 8.17%
- Packaging & Container: 9.79%
- Paper/Forest Products: 10.13%
Food & Beverage
- Beverage (Alcoholic): 22.85%
- Beverage (Soft): 20.01%
- Food Processing: 11.97%
- Restaurant/Dining: 15.96%
Construction & Materials
- Building Materials: 13.34%
- Construction Supplies: 15.13%
- Engineering/Construction: 5.57%
- Homebuilding: 15.52%
Technology & Electronics
- Computer Services: 6.06%
- Computers/Peripherals: 22.65%
- Electrical Equipment: 7.15%
- Electronics (General): 8.15%
Healthcare
- Healthcare Products: 14.81%
- Hospitals/Healthcare Facilities: 12.45%
Energy & Environment
- Coal & Related Energy: 10.97%
- Green & Renewable Energy: 21.60%
- Environmental & Waste Services: 14.89%
Finance & Insurance
- Financial Services (Non-bank & Insurance): 16.33%
- Insurance (General): 16.43%
These are general benchmarks from NYU study. Your actual margin can vary depending on scale, geography, business model, and cost structure.
Factors that Affect Operating Profit Margin
Several factors can impact operating income margin:
1. Price-to-Value Fit
Your pricing only supports a healthy operating margin when it aligns with what customers are willing to pay and covers your costs. If you underprice to stay competitive without managing your COGS and expenses, your margin suffers.
2. Product Cost Control (COGS)
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) includes everything that goes into producing or sourcing what you sell. When raw material prices rise, suppliers become less efficient, or logistics costs spike, it directly reduces your operating profit.
Here’re tips to lower your COGS and more - all designed to improve your profit margin.
3. Operational Expense Management
Your operating expenses like salaries, rent, software, and marketing should scale smarter, not just bigger. If these grow faster than your revenue, your operating margin will decline.
4. Scalable Cost Structure
Businesses with scalable infrastructure such as automation, optimized supply chains, or fixed-cost leverage often see margins expand over time. If every growth milestone adds the same cost burden, you’re likely stuck with flat or shrinking margins.
Why is Operating Profit Margin Important?
Operating profit margin provides a clear picture of how well your company is performing based on its core operations without outside costs like interest and taxes.
By tracking and improving your operating profit margin, you can:
- Make smarter financial decisions like knowing when to reinvest, where to cut costs, or how much room you have to scale.
- Spot red flags early, such as declining margins may point to rising expenses, supply chain issues, or pricing misalignment before they impact your bottom line.
- Stay resilient, use strong margins as a buffer during slow seasons or economic uncertainty.
How to Increase Operating Profit Margin for Your Business?
Increasing operating profit margin isn’t about selling more at all costs, it’s about making your existing revenue more efficient. By tightening cost control, improving pricing, and scaling only what’s profitable, businesses can significantly boost margins without increasing risk.
1. Reduce Operating Costs That Don’t Drive Revenue
Start by auditing your largest operating expenses such as advertising, fulfillment, software subscriptions, and labor. Pause or cut underperforming ad campaigns, remove unused tools, and streamline fulfillment workflows to eliminate cost leakage that directly eats into operating profit.
2. Improve Pricing and Product-Level Profitability
Raising prices strategically, bundling products, or setting minimum order values can improve operating margin without increasing costs. Focus on products with strong contribution margins and stop scaling items that look good on revenue but underperform after operating expenses.
3. Optimize Marketing Efficiency
Lowering customer acquisition cost (CAC) has an immediate impact on operating margin. Improve conversion rates, refine targeting, and shift budget toward channels with proven profitability instead of scaling spend blindly based on ROAS alone.
4. Scale What’s Profitable, Not What’s Popular
Operating margin grows when you double down on products, channels, and customers that generate consistent operating profit. Use operating-level data to decide what to scale, fix, or cut especially as volume increases and costs compound.
The Right Way To Monitor Your Profit Margins
A good operating profit margin isn’t about hitting a single “perfect” number, it’s about understanding what’s healthy for your industry, tracking how efficiently your business runs, and making sure your margin stays stable or improves over time.
By benchmarking against your peers, controlling operating costs, pricing correctly, and scaling only what’s truly profitable, you build a business that can grow sustainably instead of chasing revenue at the expense of profit.
For eCommerce merchants, especially Shopify sellers, this becomes much easier when you can see your margins clearly and consistently. That’s where TrueProfit comes in: the #1 Shopify Profit Analytics solution built specifically for eCommerce, helping you monitor all your store’s ins and outs including gross profit, net profit, and all underlying costs in real time, so you can make confident, data-backed decisions and stay focused on what really matters to your true bottom line.

Harry Chu is the Founder of TrueProfit, a net profit tracking solution designed to help Shopify merchants gain real-time insights into their actual profits. With 11+ years of experience in eCommerce and technology, his expertise in profit analytics, cost tracking, and data-driven decision-making has made him a trusted voice for thousands of Shopify merchants.


 Shopify profits
Shopify profits