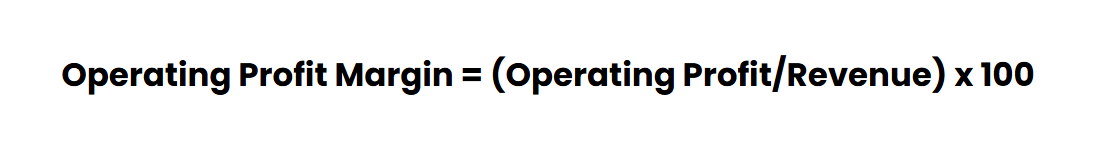Operating Profit Margin: What It Is and How to Calculate It

Operating profit margin measures the percentage of revenue after subtracting operating expenses. It does not include interest and taxes, focusing solely on profit generated from core operations.
To calculate it, divide operating income by total revenue and multiply by 100. It is a key metric for showing how efficiently a company generates profit from its operations.
In this guide, you’ll learn more about this metric step by step.
In this blog:
What is Operating Profit Margin?
Operating profit margin, often called as operating margin or operating profit percentage or operating income margin in PnL statements, measures the percentage of revenue remaining after covering operating expenses, excluding interest and taxes.
This metric includes expenses like rent, utilities, payroll, and marketing but excludes non-operational items like interest payments and income taxes.
A higher operating profit margin indicates your business is efficient at managing operational costs relative to its revenue, which is crucial for maintaining healthy profits and reinvesting in growth.
How to Calculate Operating Profit Margin Ratio?
To calculate your operating margin ratio, you just take your operating income and divide it by your revenue, then multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
Operating income (Operating profit) is what you have left after paying for the cost of goods sold (COGS) and your operating expenses (like rent, salaries, marketing, and software). It doesn’t include interest or taxes—just the costs of running your business.


For example, if you made $100,000 in sales and spent $60,000 on COGS and operating expenses combined, your operating income would be $40,000.
Then, you’d do: (40,000/100,000)×100=40%
Your operating profit margin is 40%, meaning you retain 40 cents in operating profit for every dollar earned before paying interest and taxes.
How to Use Operating Profit Percentage?
You can use operating profit margin as a key business performance metric - guiding decisions on pricing, cost management, and overall profitability.
1. Control Operational Cost
If your margin is high, it means you’re managing your operating expenses well relative to your revenue. If it’s low, you may need to review costs like payroll, rent, or marketing.
2. Adjust Pricing Strategy
It helps you see if your current pricing strategy covers your operating costs while leaving enough room for profit. If your margin is thin, you may need to adjust prices or find ways to reduce operational expenses.
3. Track Business Health Over Time
By monitoring your margin regularly, you can spot trends. A declining margin might signal rising costs or pricing challenges. Regularly tracking this metric alongside your gross profit margin and net profit margin gives a comprehensive profitability analysis.
What is a Good Operating Profit Margin?
A good operating profit margin is around 10% (average) to 20% (excellent), depending on your industry and debt levels.
Remember, operating margin is only truly good if your debt and interest payments are under control so your operating profits can translate into real net profit and healthy cash flow.
Why Is Operating Profit Percentage Important?
Expressed as percentage, operating margin shows the profit your business generates from every dollar of sales, after covering both the cost to produce goods and the expenses to run daily operations. A higher margin means you’re keeping more profit while managing costs well.
By including these costs, the metric gives you a fuller, more realistic picture of your business’s profitability than gross margin.
What are Limitations of Operating Profit Margin?
Operating profit margin doesn’t include interest expenses or taxes, so while it shows how your core operations are performing, it doesn’t reflect your actual net profit.
It also ignores non-operating income, like investment gains, which can sometimes play a big role in your overall profit optimization.
How Can Companies Improve Their Operating Profit Margin?
1. Raise Prices Strategically
Raising prices can increase your margins, but it’s not something to rush.
Raising too fast without clear value can lead to resistance, refunds, or lost customers.
Pricing adjustments can be sensitive. But if customers feel they’re getting consistent value—speed, clarity, ease, and care—they see your product as something worth paying for. A price increase now feels less like an extra cost and more like a fair exchange.
2. Negotiate with Suppliers
The win isn’t in demanding a discount; it’s in creating a win-win deal that lowers your COGS while making your supplier a partner in your growth.
Come prepared with your order history and payment track record so they see you’re a serious, reliable customer. Show them you’re ready to grow together, and you’ll often find they’re open to better pricing or terms.
3. Upsell and Cross-sell
Selling more to existing customers is often more cost-effective than finding new ones, helping protect and grow your margins.
Look for opportunities to offer upgrades, complementary products, or bundles that genuinely add value to your customers. If you’re in eCommerce, this could mean offering a premium version, faster shipping options, or product pairings customers often buy together.
4. Monitor Regularly
Your operating margin isn’t something you check once. By monitoring it regularly alongside these ecommerce metrics, you can catch rising costs, see the impact of pricing changes, and adjust quickly if trends shift. It helps you spot inefficiencies before they become big problems.
Understanding your operating profit margin is a cornerstone for managing a profitable business. By tracking it regularly, using the clear formula, and leveraging analytics tools, you’ll gain better control over your operational costs and pricing decisions.
Irene Le is the Content Manager at TrueProfit, specializing in crafting insightful, data-driven content to help eCommerce merchants scale profitably. With over 5 years of experience in content creation and growth strategy for the eCommerce industry, she is dedicated to producing high-value, actionable content that empowers merchants to make informed financial decisions.

 Shopify profits
Shopify profits