Good Gross Profit Margins for Ecom in 2026 (Based on 5,000+ Stores)

In 2026, ecommerce is no longer about who can scale the fastest, it’s about who can scale profitably.
Ad costs are higher. Fulfillment is more complex. Competition is global.
That makes gross profit margin one of the most important numbers every ecommerce business needs to understand clearly.
Using TrueProfit’s analysis of how 5000+ ecommerce stores perform in 2025, this guide breaks down what a good gross profit margin looks like for ecommerce in 2026, how it varies by business model, and where your store should realistically aim to stay profitable while scaling.
In this blog:
What Is a Good Gross Profit Margin for Ecommerce in 2026?
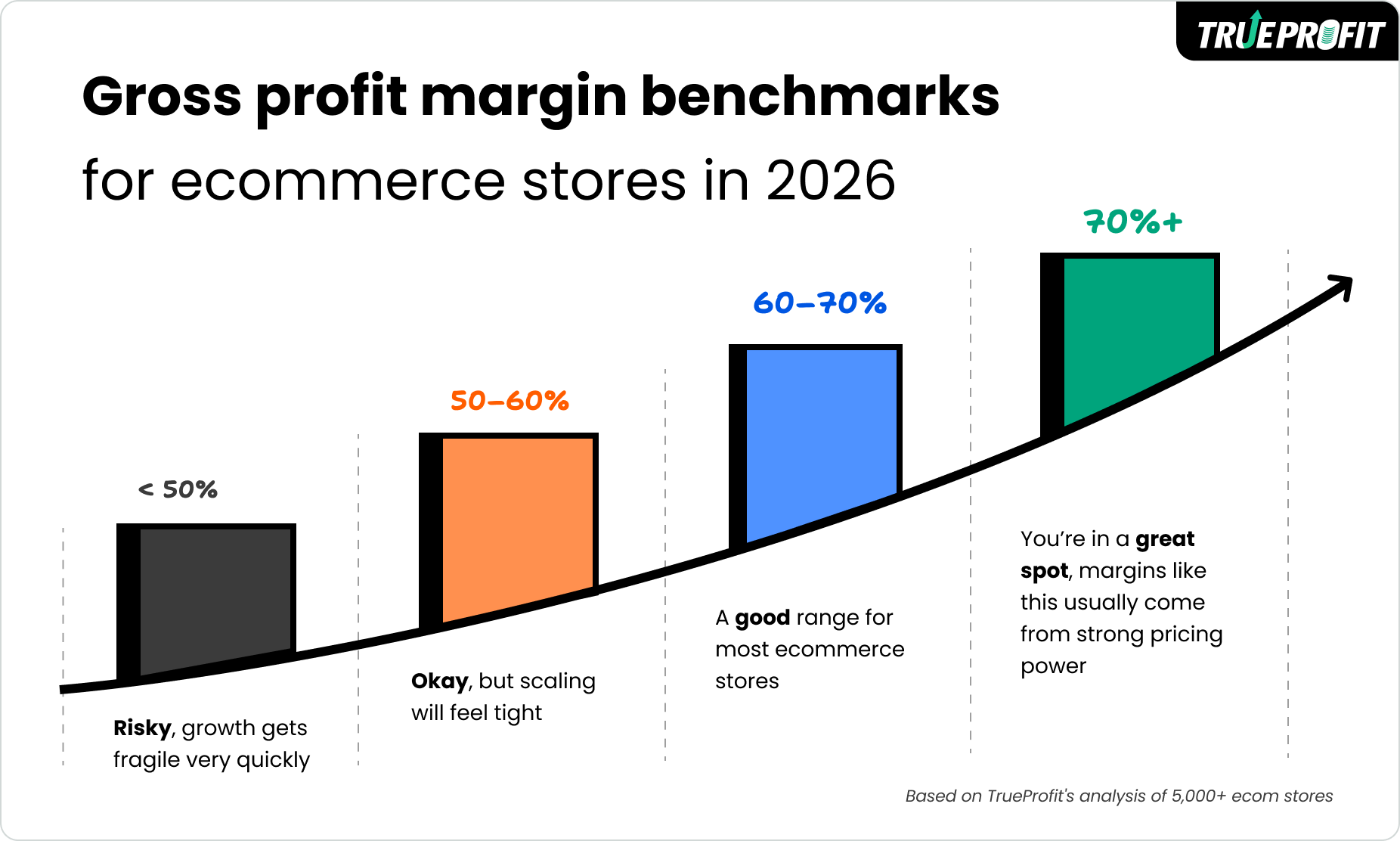
Based on TrueProfit’s analysis of more than 5,000 ecommerce stores across all industries, a gross profit margin in the 60–70% range is what makes profitable scaling possible.
Here is the gross margin benchmark for ecom stores in 2026:
- 70%+: You’re in a great spot, margins like this usually come from strong pricing power
- 60–70%: A solid, sustainable range for most ecommerce stores
- 50–60%: You can operate here, but scaling will feel tight
- Under 50%: Growth gets fragile very quickly
The average store today operates around 60–65% gross margin. Brands that sit comfortably in this range or slightly above it tend to have enough breathing room to grow without constantly running into cash flow or margin pressure.
When gross margins fall below 55%, growth becomes fragile. Scaling starts to rely heavily on volume, and even small increases in ad costs or fulfillment fees can erase profitability. Margins above 70%, while excellent, usually require strong branding, differentiated products, or clear pricing power.
This range matters because ecommerce comes with constant cost fluctuations. Ad performance shifts, fulfillment gets more expensive, refunds happen, and platform fees change. A 60–70% gross margin gives businesses the flexibility to absorb those swings and scale without watching profit collapse.
Average Gross Profit Margin for Ecommerce by Business Models
Gross profit margin doesn’t just depend on what you sell, it’s heavily shaped by how your ecommerce business is set up.
Looking at our 2025 data across thousands of ecommerce stores, different business models show very different margin patterns. Each model comes with its own trade-offs, and understanding them helps set more realistic expectations.
Dropshipping tends to sit on the higher end. With no inventory to hold and flexible sourcing, many dropshipping stores operate around 65–70% gross margin. The trade-off is that these margins can disappear quickly if ad performance drops or competition pushes costs up.
Self-produced or private label brands usually fall slightly lower, around 60–65%. While margins may not look as high on paper, these businesses benefit from stronger control over production costs and pricing. Over time, that often leads to more stable margins though it does require upfront investment and tighter operations.
Print-on-demand (POD) businesses also tend to land in the 60–65% range. Fulfillment is simple and scalable, but base production costs are higher. For POD brands, margins are often protected through branding, bundling, and upsells rather than product cost alone.
Business Model | Average gross profit margin | What to Expect |
|---|---|---|
Dropshipping | 65–70% | Higher markups and low inventory risk, but sensitive to ad performance |
Self-produced / Private Label | 60–65% | More control and long-term stability, with higher upfront investment |
Print on Demand (POD) | 60–65% | Simple fulfillment, but margins rely heavily on branding and upsells |
Factors That Affect Gross Profit Margin in Ecommerce
Gross profit margin isn’t a fixed number you set once and forget. It shifts constantly, shaped by the everyday decisions you make across sourcing, pricing, and operations.
1. Product Cost & Supplier Pricing
Product cost sits at the foundation of your margin. Even small increases from suppliers can quietly destroy profitability once you start scaling. That’s why ongoing supplier negotiation, volume discounts, and avoiding reliance on a single supplier become more important as your business grows.
2. Pricing Strategy
Underpricing is one of the fastest ways ecommerce businesses bleed profit without realizing it. Heavy discounting, offering free shipping without a margin buffer, or competing purely on price might boost short-term sales, but over time they steadily compress gross profit margin and make sustainable growth harder.
3. Product Mix
Not all products are meant to make the same amount of money. In most ecommerce stores, high-margin products quietly subsidize lower-margin “hero” products that drive volume or traffic. Healthy stores balance entry products with core profit drivers, plus higher-margin add-ons or bundles that lift overall margins.
4. Fulfillment & Logistics
Fulfillment decisions directly affect gross profit, even if they don’t always feel like part of COGS. Shipping rates, packaging choices, and return policies all add up. Poor logistics decisions rarely hurt all at once, they slowly eat into gross margin month after month.
5. Operational Efficiency
As volume increases, inefficiencies compound fast. Manual workflows, weak inventory planning, and fulfillment errors create hidden costs that don’t always show up immediately, but eventually surface as margin leakage. Improving efficiency is often one of the simplest ways to protect gross profit at scale.
How to Increase Gross Profit Margin for Ecommerce Businesses?
Improving gross profit margin doesn’t always mean charging more. In practice, the biggest margin gains usually come from fixing leaks, not squeezing customers.
1. Optimize Product Costs (This Is Where Margin Is Won or Lost)
Product cost is the foundation of your margin, and small changes here compound fast at scale. A 3–5% cost reduction often does more for profit than a major pricing experiment.
Revisit supplier terms regularly, especially once volume increases. Consolidating SKUs can unlock better pricing and simplify operations at the same time. Just as importantly, don’t be afraid to cut low-margin products that look good on revenue but quietly drain cash and attention.
If a product can’t improve margin after a few iterations, it’s usually better to let it go.
2. Improve Pricing Intelligence (Stop Discounting by Default)
Most ecommerce stores underprice because they’re afraid to test. Discounting feels safe, but it slowly trains customers to expect less margin.
Instead of defaulting to sales, test price elasticity on your best-selling products. Bundle complementary items to increase perceived value. Introduce premium versions that give customers a reason to pay more without hurting your base offer.
Often, the goal isn’t to raise prices across the board, it’s to give profitable customers a better option to say yes to.
3. Reduce Fulfillment Waste (The Silent Margin Killer)
Fulfillment costs rarely break margins overnight, they erode them quietly. Shipping zones, carrier selection, packaging size, and materials all act like hidden COGS.
Audit fulfillment regularly. Look for products that ship inefficiently or return too often. Many return issues come from unclear product pages, inaccurate sizing, or mismatched expectations, not from bad customers.
Every percentage point saved here drops straight to gross profit.
4. Focus on High-Margin SKUs (Revenue Isn’t the Goal, Profit Is)
A common scaling mistake is pushing products that grow revenue but don’t grow profit. Many stores would scale faster by selling fewer products more intentionally.
Identify the SKUs that already deliver strong margins and stable demand. Double down on those before launching something new. New products add complexity; profitable products buy you time and flexibility.
How to Track Profit Margin for Ecommerce Businesses
Knowing what a good gross profit margin should be is useless if you can’t track it accurately.
Many ecommerce businesses:
- Track revenue daily
- Watch ROAS obsessively
- But don’t see real gross margin in real time
Spreadsheets break as volume grows. Manual tracking misses refunds, shipping adjustments, transaction fees, and partial refunds.
To scale profitably in 2026, ecommerce founders need:
- Real-time profit visibility
- Margin tracking by product, order, and channel
- Clear separation between revenue and actual profitability
If you’re running a Shopify store, TrueProfit is the #1 Shopify Profit Analytics app that automatically tracks your profit and loss in real time, giving you clear, actionable insights instead of spreadsheet guesswork.
In a market where revenue is easy to fake but profit is hard to protect, margin clarity becomes a competitive advantage in 2026.
Irene Le is the Content Manager at TrueProfit, specializing in crafting insightful, data-driven content to help eCommerce merchants scale profitably. With over 5 years of experience in content creation and growth strategy for the eCommerce industry, she is dedicated to producing high-value, actionable content that empowers merchants to make informed financial decisions.







 Shopify profits
Shopify profits