What Is Total Sales and How To Calculate It? (2026)

For any business, total sales is one of the first figures shown on a profit and loss (P&L) report and reflects the total income earned during a specific period before any expenses are deducted.
This article explores what total sales represent, how they are calculated, what qualifies as “good” or “bad” sales, and why comparing total sales with net profit provides a more accurate understanding of financial performance.
In this blog:
What Is Total Sales?
Total sales represent the full amount of money a business earns from selling its products or services before subtracting costs such as ad spend, shipping costs, product costs (COGS), etc. It’s also commonly referred to as total revenue, gross sales, or the top line in financial reporting.
When evaluating business total sales offers a direct measure of sales activity and scale, allowing retailers to evaluate how effectively their products generate income.


What Is the Total Sales Formula?
Total sales are calculated by multiplying the price per unit by the number of units sold. For stores with multiple products, calculate the sales for each item and add them together.
For businesses selling a single product, this calculation is direct. For example, selling 100 mugs at $10 each results in $1,000 in total sales. Multi-product stores need to calculate revenue for each product individually and then sum the results. The total will reflect the complete revenue picture generated by the business over that period.
What Is a Good Number of Sales?
Defining what counts as “good” sales is not as simple as looking at the number of transactions. The value of sales depends heavily on the type of product, the average selling price, and the business model.
For example, a SaaS dealer may close only 20 sales in a year, yet each transaction generates hundreds of thousands of dollars. With strong margins, this small sales volume translates into substantial profit. Meanwhile, a small retailer selling keychains might record 50 sales per day, but with low prices and slim margins, the business may struggle to stay profitable despite the higher transaction count.
This contrast highlights an important truth: good sales are relative. The measure of sales quality lies not in quantity but in whether they align with financial objectives and contribute to profitability.
For most retailers, a practical way to define “good” sales is to begin with revenue goals. How much income does the business aim to generate per year, per month, or even per day? Once that target is clear, total sales can be evaluated against it.
What Is Bad Sales?
Just as there is no universal benchmark for good sales, there is no simple number that defines bad sales. What qualifies as “bad” depends on context, and the raw number of transactions volume rarely tells the full story.
In practice, bad sales are those that do not align with financial objectives. If revenue cannot cover expenses such as product costs, shipping, advertising, and overhead, the sales achieved—no matter how impressive they appear—do not drive the true business growth.
Ultimately, a “good” or bad level of sales depends on whether the transaction counts support the business’s growth strategy and ensures profitability. Sales volume, on its own, offers little value without being tied to profit outcomes.
Total Sales vs. Net Profit: What’s the Difference?
Total sales and net profit are two of the most important financial metrics, and when analyzed together, they provide a clear picture of a business’s overall health.
The distinction is simple but critical: total sales is the full income generated from selling products or services before any expenses are deducted. While net profit, also known as the “bottom line” , is what remains after subtracting all costs, including product costs (COGS), advertising spend, shipping, refunds, and operating expenses.
Like we said above, total sales alone cannot reveal your accurate income. By examining total sales and net profit together, retailers gain both perspectives—the scale of sales volume and the actual value created from those sales. Together, these metrics will provide the complete view needed to make smarter, data-driven decisions that truly bring meaningful business growth.
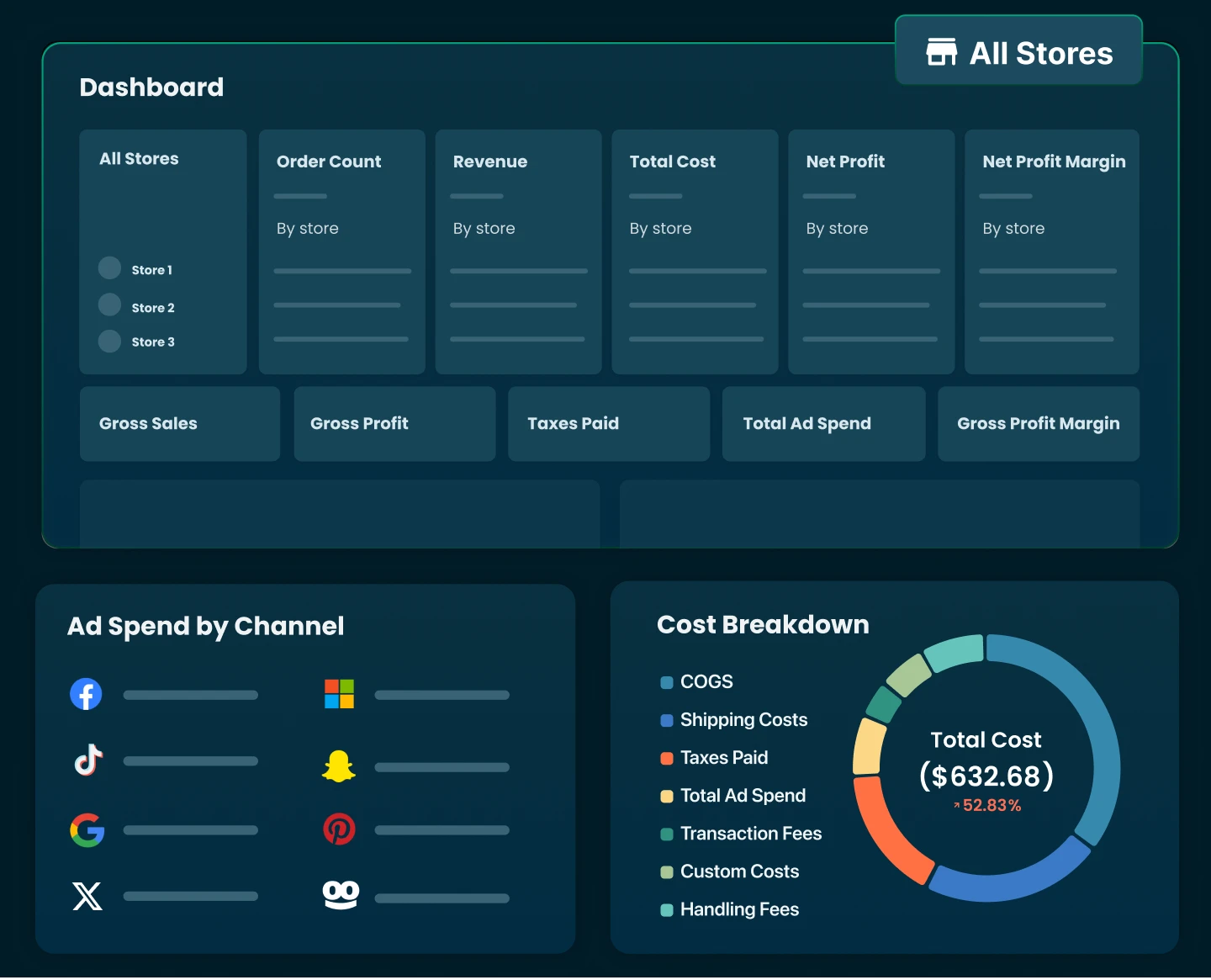
This is where TrueProfit provides an advantage. As a leading net profit analytics tool for Shopify, TrueProfit consolidates every essential financial metric—total sales, total costs, and profit—into one real-time dashboard.
With TrueProfit, Shopify sellers can see not only how much their store sold, but also whether those sales generated profit. This clarity allows businesses to move beyond vanity metrics and focus on sustainable growth, informed by accurate financial insights.
Final Thoughts
Total sales are the foundation of financial reporting, offering a simple yet essential measure of sales activity. However, sales volume alone cannot reveal whether a business is truly successful. Evaluating total sales alongside net profit provides the most accurate picture of financial health.
Irene Le is the Content Manager at TrueProfit, specializing in crafting insightful, data-driven content to help eCommerce merchants scale profitably. With over 5 years of experience in content creation and growth strategy for the eCommerce industry, she is dedicated to producing high-value, actionable content that empowers merchants to make informed financial decisions.



 Shopify profits
Shopify profits